Detecting h-index manipulation through self-citation analysis
- PMID: 21472020
- PMCID: PMC3043246
- DOI: 10.1007/s11192-010-0306-5
Detecting h-index manipulation through self-citation analysis
Abstract
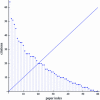
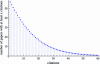
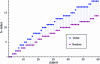
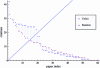
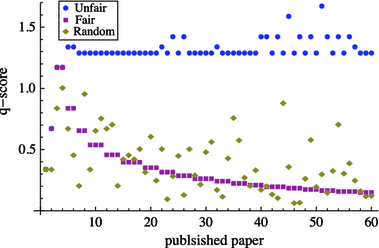
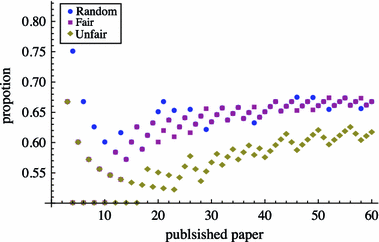
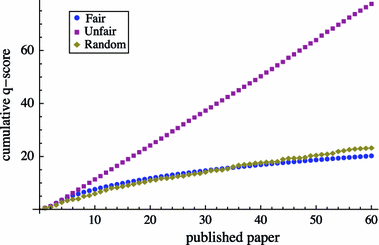
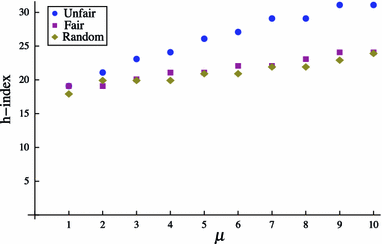
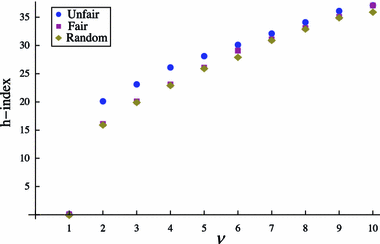
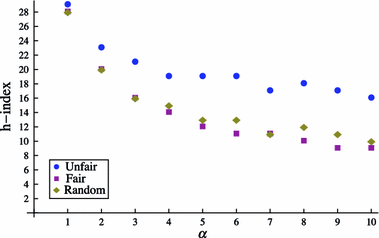
The h-index has received an enormous attention for being an indicator that measures the quality of researchers and organizations. We investigate to what degree authors can inflate their h-index through strategic self-citations with the help of a simulation. We extended Burrell's publication model with a procedure for placing self-citations, following three different strategies: random self-citation, recent self-citations and h-manipulating self-citations. The results show that authors can considerably inflate their h-index through self-citations. We propose the q-index as an indicator for how strategically an author has placed self-citations, and which serves as a tool to detect possible manipulation of the h-index. The results also show that the best strategy for an high h-index is publishing papers that are highly cited by others. The productivity has also a positive effect on the h-index.
Figures
References
-
- Aksnes D. A macro study of self-citation. Scientometrics. 2003;56(2):235–246. doi: 10.1023/A:1021919228368. - DOI
-
- Burrell Q. L. Should the h-index be discounted? ISSI Newsletter. 2007;3-S:65–67.
-
- Burrell Q. L. Hirsch’s h-index: A stochastic model. Journal of Informetrics. 2007;1(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2006.07.001. - DOI
-
- Egghe L. Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics. 2006;69(1):131–152. doi: 10.1007/s11192-006-0144-7. - DOI
-
- Garcia-Perez M. A multidimensional extension to Hirschs h-index. Scientometrics. 2009;81(3):779–785. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-2290-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
