Rehabilitating a brain with Alzheimer's: a proposal
- PMID: 21472092
- PMCID: PMC3066253
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S14008
Rehabilitating a brain with Alzheimer's: a proposal
Abstract
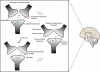
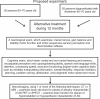
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, originating sporadically in the population aged over 65 years, and advanced age is the principal risk factor leading to AD development. In spite of the large amount of research going on around the globe and all the information now available about AD, there is still no origin or triggering process known so far. Drugs approved for the treatment of AD include tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine, and memantine. These may delay or slow down the degenerative process for a while, but they can neither stop nor reverse its progression. Because that this might be due to a lack of effect of these drugs on degenerating neurons, even when they are able to potentiate the brain in nondegenerative conditions, we propose here an alternative therapy consisting of initial repair of neuronal membranes followed by conventional drug therapies. The rehabilitation of neurons in a degeneration process would enable the drugs to act more effectively on them and improve the effects of treatment in AD patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer; drugs; rehabilitation.
Figures

References
-
- Perez-Tur J. Genetics and Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurol. 2000;30:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Lopez de Munain A. Classification of mitochondrial diseases. Rev Neurol. 1998;26(Suppl 1):S9–S14. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Allsop D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991;12:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Jarrett JT, Lansbury PTJ. Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: A pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie. Cell. 1993;73:1055–1058. - PubMed
-
- Hu X, Hicks CW, He W, et al. BACE1 modulates myelination in the central and peripheral nervous system. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1520–1525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

