Imprinted tumor suppressor gene ARHI induces apoptosis correlated with changes in DNA methylation in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 21472283
- PMCID: PMC3097896
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr_00000301
Imprinted tumor suppressor gene ARHI induces apoptosis correlated with changes in DNA methylation in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
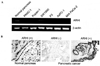
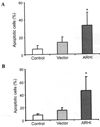
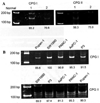
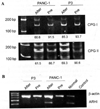
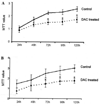
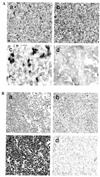
Aplesia Ras homologue member I (ARHI, DIRAS3) is a Ras-related imprinted growth inhibitory gene whose expression is down-regulated in the majority of breast and ovarian cancers. This study investigated the inhibitory function of ARHI in pancreatic cancer. Six pancreatic cancer cell lines, tumor xenografts in nude mice and 20 pancreatic cancer tissue sections were analyzed. ARHI is widely expressed in ductal and acinar cells of normal pancreatic tissue, but is down-regulated or lost in approximately 50% of pancreatic cancers. Aberrant methylation of the ARHI locus was found in five pancreatic cancer cell lines, which exhibited down-regulation or loss of ARHI expression. Hypermethylation was detected in five cell lines (5/5, 100%) at CpG island I, in two cell lines (2/5, 40%) at CpG island II and in four cell lines (4/5, 80%) at CpG island III. Re-expression of ARHI significantly inhibited the growth of pancreatic cancer cells. This inhibition was associated with the induction of apoptosis. Treatment with the demethylating agent 5-aza-2'deoxycytidine (5-aza-dC) restored ARHI mRNA expression, inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis in PANC-1 and P3 human pancreatic cancer cells in culture. In nu/nu mice, 5-aza-dC also inhibited the growth of PANC-1 xenografts and induced apoptosis, as observed by TUNEL staining. These effects were associated with the re-expression of ARHI protein. Therefore, ARHI may serve as a growth inhibitory gene in a significant fraction of pancreatic cancers. Re-expression of ARHI significantly induced the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. A demethylation agent reduced human pancreatic cancer cell line growth in conjunction with ARHI re-expression.
Figures
References
-
- Smakman N, Borel Rinkes IH, Voest EE, Kranenburg O. Control of colorectal metastasis formation by K-Ras. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1756:103–114. - PubMed
-
- Kranenburg O. The KPAS oncogene: past, present, and future. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1756:81–82. - PubMed
-
- Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G. Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:295–308. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani SR, Petricoin EF, Maitra A, et al. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:437–450. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

