Matrix pre-coated MALDI MS targets for small molecule imaging in tissues
- PMID: 21472558
- PMCID: PMC4151471
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-010-0013-8
Matrix pre-coated MALDI MS targets for small molecule imaging in tissues
Abstract
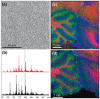
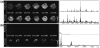
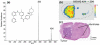
A new sample preparation method for MALDI tissue imaging has been developed for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds that employs matrix pre-coated MALDI targets. Tissue sections need only to be transferred onto the pre-coated target before analysis for fast and easy sample preparation. Pre-coated targets have a homogenous matrix coating with uniform crystals of approximately 1-2 μm and do not require solvents that may lead to analyte delocalization within a tissue section. We report here the use of matrix pre-coated targets for imaging of lipids, peptides, and pharmaceuticals in tissues.
© American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2011
Figures
References
-
- Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 1997;69(23):4751–4760. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Caprioli RM. Direct profiling and imaging of peptides and proteins from mammalian cells and tissue sections by mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis. 2002;23(18):3125–3135. - PubMed
-
- Khatib-Shahidi S, Andersson M, Herman JL, Gillespie TA, Caprioli RM. Direct molecular analysis of whole-body animal tissue sections by imaging MALDI mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006;78(18):6448–6456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

