MicroRNA profiling of adrenocortical tumors reveals miR-483 as a marker of malignancy
- PMID: 21472710
- PMCID: PMC3051015
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25724
MicroRNA profiling of adrenocortical tumors reveals miR-483 as a marker of malignancy
Abstract
Background: The authors are interested in identifying molecular markers that can aid in the diagnosis of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC). The aim of this study was to identify microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) that are differentially expressed in malignant adrenocortical tumors as compared with benign tumors and assess their potential as diagnostic predictors.
Methods: Differentially expressed miRNAs were identified using microarray profiling of adrenocortical tumors and validated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
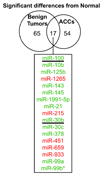
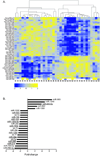
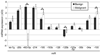
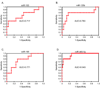
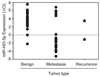
Results: Microarray profiling in benign and primary malignant adrenocortical tumors revealed several significant differences between these histological groups. By using directed quantitative RT-PCR analysis on a subset of these differentially expressed miRNAs, the authors determined that miRs -100, -125b, and -195 were significantly down-regulated, whereas miR-483-5p was significantly up-regulated in malignant as compared with benign tumors. Furthermore, the current study shows that miR-483-5p expression can accurately categorize tumors as benign or malignant.
Conclusions: The authors identified 4 miRNAs that are dysregulated in adrenocortical carcinoma. The high expression of one of these, miR-483-5p, appears to be a defining characteristic of adrenocortical malignancies, and can thus be used to accurately distinguish between benign and malignant adrenocortical tumors.
Copyright © 2010 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Icard P, Goudet P, Charpenay C, Andreassian B, Carnaille B, Chapuis Y, et al. Adrenocortical carcinomas: surgical trends and results of a 253-patient series from the French Association of Endocrine Surgeons study group. World J Surg. 2001. pp. 891–897. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Favia G, Lumachi F, Carraro P, D'Amico DF. Adrenocortical carcinoma. Our experience. Minerva Endocrinol. 1995. pp. 95–99. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Wajchenberg BL, Albergaria Pereira MA, Medonca BB, Latronico AC, Campos Carneiro P, Alves VA, et al. Adrenocortical carcinoma: clinical and laboratory observations. Cancer. 2000. pp. 711–736. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Brunt LM, Moley JF. Adrenal incidentaloma. World J Surg. 2001. pp. 905–913. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Lau SK, Weiss LM. The Weiss system for evaluating adrenocortical neoplasms: 25 years later. Hum Pathol. 2009. pp. 757–768. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

