Chromosomal radiosensitivity and acute radiation side effects after radiotherapy in tumour patients--a follow-up study
- PMID: 21473753
- PMCID: PMC3080817
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-32
Chromosomal radiosensitivity and acute radiation side effects after radiotherapy in tumour patients--a follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapists are highly interested in optimizing doses especially for patients who tend to suffer from side effects of radiotherapy (RT). It seems to be helpful to identify radiosensitive individuals before RT. Thus we examined aberrations in FISH painted chromosomes in in vitro irradiated blood samples of a group of patients suffering from breast cancer. In parallel, a follow-up of side effects in these patients was registered and compared to detected chromosome aberrations.
Methods: Blood samples (taken before radiotherapy) were irradiated in vitro with 3 Gy X-rays and analysed by FISH-painting to obtain aberration frequencies of first cycle metaphases for each patient. Aberration frequencies were analysed statistically to identify individuals with an elevated or reduced radiation response. Clinical data of patients have been recorded in parallel to gain knowledge on acute side effects of radiotherapy.
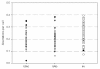
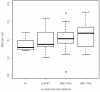
Results: Eight patients with a significantly elevated or reduced aberration yield were identified by use of a t-test criterion. A comparison with clinical side effects revealed that among patients with elevated aberration yields one exhibited a higher degree of acute toxicity and two patients a premature onset of skin reaction already after a cumulative dose of only 10 Gy. A significant relationship existed between translocations in vitro and the time dependent occurrence of side effects of the skin during the therapy period.
Conclusions: The results suggest that translocations can be used as a test to identify individuals with a potentially elevated radiosensitivity.
Figures

References
-
- Barber JB, Burrill W, Spreadborough AR, Levine E, Warren C, Kiltie AE, Roberts SA, Scott D. Relationship between in vitro chromosomal radiosensitivity of peripheral blood lymphocytes and the expression of normal tissue damage following radiotherapy for breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2000;55:179–186. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(99)00158-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sprung CN, Davey DS, Withana NP, Distel LV, McKay MJ. Telomere length in lymphoblast cell lines derived from clinically radiosensitive cancer patients. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008. pp. 638–644. - PubMed
-
- Dyomina EA, Ryabchenko NM. Increased individual chromosomal radiosensitivity of human lymphocytes as a parameter of cancer risk. Exp Oncol. 2007;29:217–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

