Highly efficient miRNA-mediated reprogramming of mouse and human somatic cells to pluripotency
- PMID: 21474102
- PMCID: PMC3090650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.03.001
Highly efficient miRNA-mediated reprogramming of mouse and human somatic cells to pluripotency
Erratum in
- Cell Stem Cell. 2012 Dec 7;11(6):853
Abstract
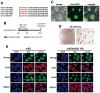
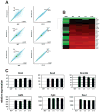
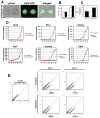
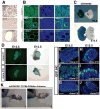
Transcription factor-based cellular reprogramming has opened the way to converting somatic cells to a pluripotent state, but has faced limitations resulting from the requirement for transcription factors and the relative inefficiency of the process. We show here that expression of the miR302/367 cluster rapidly and efficiently reprograms mouse and human somatic cells to an iPSC state without a requirement for exogenous transcription factors. This miRNA-based reprogramming approach is two orders of magnitude more efficient than standard Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/Myc-mediated methods. Mouse and human miR302/367 iPSCs display similar characteristics to Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/Myc-iPSCs, including pluripotency marker expression, teratoma formation, and, for mouse cells, chimera contribution and germline contribution. We found that miR367 expression is required for miR302/367-mediated reprogramming and activates Oct4 gene expression, and that suppression of Hdac2 is also required. Thus, our data show that miRNA and Hdac-mediated pathways can cooperate in a powerful way to reprogram somatic cells to pluripotency.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
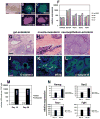
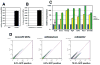
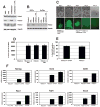
Comment in
-
Small RNAs loom large during reprogramming.Cell Stem Cell. 2011 Jun 3;8(6):599-601. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.05.009. Cell Stem Cell. 2011. PMID: 21624799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS, Sander C. The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D149–153. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

