Abuse liability profile of three substituted tryptamines
- PMID: 21474568
- PMCID: PMC3126641
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.111.179705
Abuse liability profile of three substituted tryptamines
Abstract
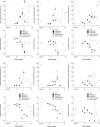
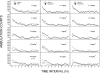
The abuse liability profile of three synthetic hallucinogens, N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (DIPT), 5-N,N-diethyl-5-methoxytryptamine (5-MeO-DET), and 5-methoxy-α-methyltryptamine (5-MeO-AMT), was tested in rats trained to discriminate hallucinogenic and psychostimulant compounds, including cocaine, methamphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethylamphetamine (MDMA), lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), (-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM), and dimethyltryptamine (DMT). Because abused hallucinogens act at 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A (5-HT(1A)) and 5-HT(2A) receptors, and abused psychostimulants act at monoamine transporters, binding and functional activities of DIPT, 5-MeO-DET, and 5-MeO-AMT at these sites were also tested. DIPT fully substituted in rats trained to discriminate DMT (ED(50) = 1.71 mg/kg) and DOM (ED(50) = 1.94 mg/kg), but produced only 68% LSD-appropriate responding. 5-MeO-DET fully substituted for DMT (ED(50) = 0.41 mg/kg) and produced 59% MDMA-appropriate responding. 5-MeO-AMT did not fully substitute for any of the training drugs, but produced 67% LSD-appropriate responding. None of the compounds produced substitution in rats trained to discriminate cocaine or methamphetamine. All three compounds showed activity at 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2A) receptors as well as blockade of reuptake by the serotonin transporter. In addition, 5-MeO-AMT produced low levels of serotonin release and low potency blockade of dopamine uptake. DIPT, 5-MeO-DET, and 5-MeO-AMT produced behavioral and receptor effects similar to those of abused hallucinogens, but were not similar to those of psychostimulants. DIPT and 5-MeO-DET may have abuse liability similar to known hallucinogens and may be hazardous because high doses produced activity and lethality.
Figures
References
-
- Adkins EM, Barker EL, Blakely RD. (2001) Interactions of tryptamine derivatives with serotonin transporter species variants implicate transmembrane domain I in substrate recognition. Mol Pharmacol 59:514–523 - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108 - PubMed
-
- Cozzi NV, Gopalakrishnan A, Anderson LL, Feih JT, Shulgin AT, Daley PF, Ruoho AE. (2009) Dimethyltryptamine and other hallucinogenic tryptamines exhibit substrate behavior at the serotonin uptake transporter and the vesicle monoamine transporter. J Neural Transm 116:1591–1599 - PubMed
-
- Deneau G, Yanagita T, Seevers MH. (1969) Self-administration of psychoactive substances by the monkey. Psychopharmacologia 16:30–48 - PubMed
-
- Eshleman AJ, Carmolli M, Cumbay M, Martens CR, Neve KA, Janowsky A. (1999) Characteristics of drug interactions with recombinant biogenic amine transporters expressed in the same cell type. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:877–885 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

