A rapid generalized least squares model for a genome-wide quantitative trait association analysis in families
- PMID: 21474944
- PMCID: PMC3080778
- DOI: 10.1159/000324839
A rapid generalized least squares model for a genome-wide quantitative trait association analysis in families
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using family data involve association analyses between hundreds of thousands of markers and a trait for a large number of related individuals. The correlations among relatives bring statistical and computational challenges when performing these large-scale association analyses. Recently, several rapid methods accounting for both within- and between-family variation have been proposed. However, these techniques mostly model the phenotypic similarities in terms of genetic relatedness. The familial resemblances in many family-based studies such as twin studies are not only due to the genetic relatedness, but also derive from shared environmental effects and assortative mating. In this paper, we propose 2 generalized least squares (GLS) models for rapid association analysis of family-based GWAS, which accommodate both genetic and environmental contributions to familial resemblance. In our first model, we estimated the joint genetic and environmental variations. In our second model, we estimated the genetic and environmental components separately. Through simulation studies, we demonstrated that our proposed approaches are more powerful and computationally efficient than a number of existing methods are. We show that estimating the residual variance-covariance matrix in the GLS models without SNP effects does not lead to an appreciable bias in the p values as long as the SNP effect is small (i.e. accounting for no more than 1% of trait variance).
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
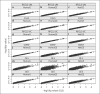
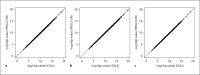
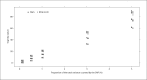


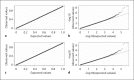
References
-
- Benyamin B, Visscher PM, McRae AF. Family-based genome-wide association studies. Pharmacogenomics. 2009;10:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, Rioux JD, Silverberg MS, Daly MJ, Steinhart AH, Abraham C, Regueiro M, Griffiths A, Dassopoulos T, Bitton A, Yang H, Targan S, Datta LW, Kistner EO, Schumm LP, Lee AT, Gregersen PK, Barmada MM, Rotter JI, Nicolae DL, Cho JH. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science. 2006;314:1461–1463. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

