Overlapping presence of macroamylasemia and hyperamylasemia in acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 21474984
- PMCID: PMC3116008
- DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.2.98
Overlapping presence of macroamylasemia and hyperamylasemia in acute pancreatitis
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
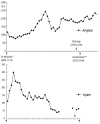
Figures


Similar articles
-
A correlation between clinical pancreatitis and isoenzyme patterns of amylase.Surgery. 1982 Oct;92(4):576-80. Surgery. 1982. PMID: 6181574
-
Lipase and pancreatic amylase activities in diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in patients with hyperamylasemia.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005 Nov;4(4):600-3. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005. PMID: 16286272
-
Factors affecting pancreatic hyperamylasemia in patients undergoing peroral single-balloon enteroscopy.Dig Endosc. 2015 Sep;27(6):674-8. doi: 10.1111/den.12449. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Dig Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25630832
-
[Macroamylasemia in the differential diagnosis of acute pancreatitis].Rev Clin Esp. 1999 Jul;199(7):440-1. Rev Clin Esp. 1999. PMID: 10481560 Review. Spanish.
-
[Macroamylasemia: its current and clinical importance].Rev Clin Esp. 1989 May;184(8):431-4. Rev Clin Esp. 1989. PMID: 2476840 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Choi S, Ihm C, Jang S. Evaluation of the clinical usefulness for pancreatic amylase in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Lab Med. 2003;23:98–103.
-
- Sagristani M, Guariglia R, Pocali B, De Rienzo M, Guastafierro S, Romano G, et al. Macroamylasemia in a patient with multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:1705–1707. - PubMed
-
- Lankisch PG, Doobe C, Finger T, Lübbers H, Mahlke R, Brinkmann G, et al. Hyperamylasaemia and/or hyperlipasaemia: incidence and underlying causes in hospitalized patients with non-pancreatic diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:237–241. - PubMed
-
- Barera G, Bazzigaluppi E, Viscardi M, Renzetti F, Bianchi C, Chiumello G, et al. Macroamylasemia attributable to gluten-related amylase autoantibodies: a case report. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
