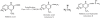Synthesis of a new series of substituted pyrimidines and its evaluation for antibacterial and antinociceptive effects
- PMID: 21475470
- PMCID: PMC3068719
Synthesis of a new series of substituted pyrimidines and its evaluation for antibacterial and antinociceptive effects
Abstract
Background: Pyrimidines are a well known group of compounds reported to have different biological activities. Prompted from the diversity of its wider use and being an integral part of genetic material, an effort was made to synthesize a novel series of amino-pyrimidine derivatives of pharmaceutical interest by condensing the guanidinyl derivative of nalidixic acid with different chalcones.
Methods: The structures of all synthesized compounds were established on the basis of IR and 1HNMR spectral studies. All of the new compounds in this series were screened for antimicrobial activity. Gram +ve and Gram -ve strains were used to ascertain the spectrum of activity. ED50 values in the tail flick test were determined and recorded. Analgesic potential of compounds by using tail flick test in SWR male mice have also revealed promising results.
Results: All of the derivatives were effective in Gram -ve test against E. coli. None of the compounds show any inhibition of Gram +ve strain S. aureus. m-Bromo substitution derivative of amino-pyrimidines showed appreciable activity against E. coli, while 2,4 dichloro and p-chloro substitution derivatives also demonstrated improved activity. Compound 4 was most potent. The order of potency for these derivatives was 4>5≥6>1>2>7>3. Parallel to antimicrobial activity, m-bromo substitution derivative showed significant (P<0.01) antinociceptive response in comparison to control, and this effect was comparable to aspirin group. Trimethoxy substitution of benzene ring demonstrated moderate activity, whereas p-bromo substitution essentially had no antinociceptive effects in mice.
Conclusion: Comparing meta- and para- bromo substitutions, there had been significant (P<0.01) difference in the antinociceptive response of both the bromo-substituted derivatives. It was observed that bromo-substitution at meta- position demonstrated comparatively higher potential for its antibacterial as well as antinociceptive properties.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity; Antinociception; Chalcones; Pyrimidine derivatives; Synthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-2-carbohydrazide derivatives.Chem Cent J. 2015 Sep 24;9(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13065-015-0121-4. eCollection 2015 Dec. Chem Cent J. 2015. PMID: 26435735 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity and Anticancer of Some New Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines and Pyrazolo[5,1-c]1,2,4-triazines.Med Chem. 2020;16(6):750-760. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190620144404. Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31218963
-
Synthesis, characterization and in silico biological activity of some 2-(N,N-dimethyl guanidinyl)-4,6-diaryl pyrimidines.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016 Jul-Sep;8(3):181-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.171678. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016. PMID: 27413345 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics and Biological Evaluation of 2-chloro-7-cyclopentyl- 7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives Against Breast Cancer.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2017;20(8):703-712. doi: 10.2174/1386207320666170724110015. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2017. PMID: 28738766
-
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel racecadotril-tetrazole-amino acid derivatives as new potent analgesic agents.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 Jun 30;16(4):341-357. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.319573. eCollection 2021 Aug. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34447443 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Significance and biological importance of pyrimidine in the microbial world.Int J Med Chem. 2014;2014:202784. doi: 10.1155/2014/202784. Epub 2014 Mar 23. Int J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25383216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stuart AL, Ayisi NK, Tourigny G, Gupta VS. Antiviral activity, antimetabolic activity, and cytotoxicity of 3’-substituted deoxypyrimidine nucleosides. J Pharm Sci. 1985;74(3):246–9. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Ramesh Ashutosh, Goyal N, Chauhan PM, Gupta S. Dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines as a new class of antileishmanial agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13(24):6678–84. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Srivastava K, Puri SK, Chauhan PM. Antimalarial activity and synthesis of new trisubstituted pyrimidines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005;15(12):3130–2. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Srivastava K, Puri SK, Chauhan PM. Antimalarial activity of 2,4,6-trisubstituted pyrimidines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005;15(7):1881–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases