Apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: diagnostic and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 21476915
- PMCID: PMC3119461
- DOI: 10.1586/egh.11.6
Apoptosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: diagnostic and therapeutic implications
Abstract
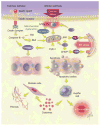
Pathological increases in cell death in the liver as well as in peripheral tissues has emerged as an important mechanism involved in the development and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). An increase in hepatocyte cell death by apoptosis is typically present in patients with NAFLD and in experimental models of steatohepatitis, while an increase in adipocyte cell death in visceral adipose tissue may be an important mechanism triggering insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. The two fundamental pathways of apoptosis, the extrinsic (death receptor-mediated) and intrinsic (organelle-initiated) pathways, are both involved. This article summarizes the current knowledge related to the distinct molecular and biochemical pathways of cell death involved in NAFLD pathogenesis. In particular, it will highlight the efforts for the development of both novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies based on this knowledge.
Figures


References
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Wieckowska A, Feldstein AE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2005;17:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, Boparai N, Liu YC, McCullough AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:1413–1419. - PubMed
-
- Harrison SA, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:861–879. ix. - PubMed
-
- Delhalle S, Duvoix A, Schnekenburger M, Morceau F, Dicato M, Diederich M. An introduction to the molecular mechanisms of apoptosis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;1010:1–8. - PubMed
Website
-
- Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Activity of GS-9450 in Adults With Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00740610.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
