Amplification of viral RNA from drinking water using TransPlex™ whole-transcriptome amplification
- PMID: 21477067
- PMCID: PMC7197749
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05029.x
Amplification of viral RNA from drinking water using TransPlex™ whole-transcriptome amplification
Abstract
Aims: Viral pathogens in environmental media are generally highly diffuse, yet small quantities of pathogens may pose a health risk. This study evaluates the ability of TransPlex™ whole transcriptome amplification (WTA) to amplify small quantities of RNA viruses from complex environmental matrices containing background nucleic acids.
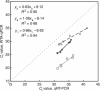
Methods and results: DNA extracts from mock drinking water samples containing mixed microbial populations were spiked with small quantities of echovirus type 13 (EV) RNA. Samples were amplified using a Transplex™ WTA kit, and EV-specific quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to quantify target pathogens before and after application of WTA. Samples amplified by WTA demonstrated a decreased limit of detection. The log-linear relationship between serial dilutions was maintained following amplification by WTA.
Conclusions: WTA is able to increase the quantity of target organism RNA in mixed populations, while maintaining log linearity of amplification across different target concentrations.
Significance and impact of the study: WTA may serve as an effective preamplification step to increase the levels of RNA prior to detection by other molecular methods such as PCR, microarrays and sequencing.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Applied Microbiology © 2011 The Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Bergen, A.W. , Haque, K.A. , Qi, Y. , Beerman, M.B. , Garcia‐Closas, M. , Rothman, N. and Chanock, S.J. (2005) Comparison of yield and genotyping performance of multiple displacement amplification and OmniPlex whole genome amplified DNA generated from multiple DNA sources. Hum Mutat 26, 262–270. - PubMed
-
- Breitbart, M. and Rohwer, F. (2005) Method for discovering novel DNA viruses in blood using viral particle selection and shotgun sequencing. BioTechniques 39, 729–736. - PubMed
-
- Chen, G. , Kobayashi, L. and Nazarenko, I. (2007) Effect of sample aliquot size on the limit of detection and reproducibility of clinical assays. Clin Chem 53, 1962–1965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

