Termination and antitermination: RNA polymerase runs a stop sign
- PMID: 21478900
- PMCID: PMC3125153
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2560
Termination and antitermination: RNA polymerase runs a stop sign
Abstract
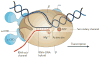
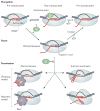
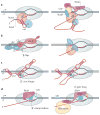
Termination signals induce rapid and irreversible dissociation of the nascent transcript from RNA polymerase. Terminators at the end of genes prevent unintended transcription into the downstream genes, whereas terminators in the upstream regulatory leader regions adjust expression of the structural genes in response to metabolic and environmental signals. Premature termination within an operon leads to potentially deleterious defects in the expression of the downstream genes, but also provides an important surveillance mechanism. This Review discusses the actions of bacterial and phage antiterminators that allow RNA polymerase to override a terminator when the circumstances demand it.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
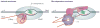

References
-
- Yin H, et al. Transcription against an applied force. Science. 1995;270:1653–1657. - PubMed
-
- Ring BZ, Yarnell WS, Roberts JW. Function of E. coli RNA polymerase σ factor σ 70 in promoter-proximal pausing. Cell. 1996;86:485–493. - PubMed
-
- Artsimovitch I, Landick R. The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell. 2002;109:193–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

