GroEL-induced topological dislocation of a substrate protein β-sheet core: a solution EPR spin-spin distance study
- PMID: 21479077
- PMCID: PMC2906716
- DOI: 10.1007/s12154-010-0038-2
GroEL-induced topological dislocation of a substrate protein β-sheet core: a solution EPR spin-spin distance study
Abstract
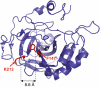
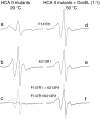
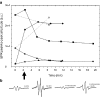
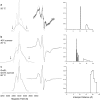
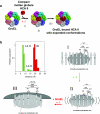
The Hsp60-type chaperonin GroEL assists in the folding of the enzyme human carbonic anhydrase II (HCA II) and protects it from aggregation. This study was aimed to monitor conformational rearrangement of the substrate protein during the initial GroEL capture (in the absence of ATP) of the thermally unfolded HCA II molten-globule. Single- and double-cysteine mutants were specifically spin-labeled at a topological breakpoint in the β-sheet rich core of HCA II, where the dominating antiparallel β-sheet is broken and β-strands 6 and 7 are parallel. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) was used to monitor the GroEL-induced structural changes in this region of HCA II during thermal denaturation. Both qualitative analysis of the EPR spectra and refined inter-residue distance calculations based on magnetic dipolar interaction show that the spin-labeled positions F147C and K213C are in proximity in the native state of HCA II at 20 °C (as close as ∼8 Å), and that this local structure is virtually intact in the thermally induced molten-globule state that binds to GroEL. In the absence of GroEL, the molten globule of HCA II irreversibly aggregates. In contrast, a substantial increase in spin-spin distance (up to >20 Å) was observed within minutes, upon interaction with GroEL (at 50 and 60 °C), which demonstrates a GroEL-induced conformational change in HCA II. The GroEL binding-induced disentanglement of the substrate protein core at the topological break-point is likely a key event for rearrangement of this potent aggregation initiation site, and hence, this conformational change averts HCA II misfolding.
Keywords: Carbonic anhydrase; Misfolding; Molecular chaperone; Molten globule; Protein aggregation; Unfoldase.
Figures
References
-
- Lambert MP, Barlow AK, Chromy BA, Edwards C, Freed R, Liosatos M, Morgan TE, Rozovsky I, Trommer B, Viola KL, Wals P, Zhang C, Finch CE, Krafft GA, Klein WL. Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:6448–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

