The role of chemokines and their receptors in angiogenesis
- PMID: 21479594
- PMCID: PMC11115067
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0677-7
The role of chemokines and their receptors in angiogenesis
Abstract
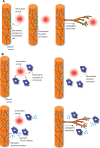
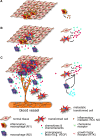
Chemokines are a vertebrate-specific group of small molecules that regulate cell migration and behaviour in diverse contexts. So far, around 50 chemokines have been identified in humans, which bind to 18 different chemokine receptors. These are members of the seven-transmembrane receptor family. Initially, chemokines were identified as modulators of the immune response. Subsequently, they were also shown to regulate cell migration during embryonic development. Here, we discuss the influence of chemokines and their receptors on angiogenesis, or the formation of new blood vessels. We highlight recent advances in our understanding of how chemokine signalling might directly influence endothelial cell migration. We furthermore examine the contributions of chemokine signalling in immune cells during this process. Finally, we explore possible implications for disease settings, such as chronic inflammation and tumour progression.
Figures
References
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature. 1997;386(6626):671–674. - PubMed
-
- Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling – in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(5):359–371. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996;380(6573):435–439. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature. 1996;380(6573):439–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

