Excess mortality in patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C treated with long-term peginterferon
- PMID: 21480316
- PMCID: PMC3073857
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24169
Excess mortality in patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C treated with long-term peginterferon
Abstract
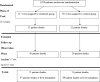
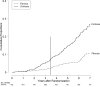
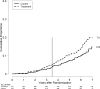
Chronic hepatitis C virus infection can cause chronic liver disease, cirrhosis and liver cancer. The Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-term Treatment against Cirrhosis (HALT-C) Trial was a prospective, randomized controlled study of long-term, low-dose peginterferon therapy in patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C who failed to respond to a previous course of optimal antiviral therapy. The aim of this follow-up analysis is to describe the frequency and causes of death among this cohort of patients. Deaths occurring during and after the HALT-C Trial were reviewed by a committee of investigators to determine the cause of death and to categorize each death as liver- or nonliver-related and as related or not to complications of peginterferon. Rates of liver transplantation were also assessed. Over a median of 5.7 years, 122 deaths occurred among 1,050 randomized patients (12%), of which 76 were considered liver-related (62%) and 46 nonliver-related (38%); 74 patients (7%) underwent liver transplantation. At 7 years the cumulative mortality rate was higher in the treatment compared to the control group (20% versus 15%, P = 0.049); the primary difference in mortality was in patients in the fibrosis compared to the cirrhosis stratum (14% versus 7%, P = 0.01); comparable differences were observed when liver transplantation was included. Excess mortality, emerging after 3 years of treatment, was related largely to nonliver-related death; liver-related mortality was similar in the treatment and control groups. No specific cause of death accounted for the excess mortality and only one death was suspected to be a direct complication of peginterferon.
Conclusion: Long-term maintenance peginterferon in patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C is associated with an excess overall mortality, which was primarily due to nonliver-related causes among patients with bridging fibrosis.
2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009;29(Suppl 1):74–81. - PubMed
-
- Lee WM, Dienstag JL, Lindsay KL, Lok AS, Bonkovsky HL, Shiffman ML, Everson GT, Di Bisceglie AM, Morgan TR, Ghany MG, Morishima C, Wright EC, Everhart JE, HALT-C Trial Group Evolution of the HALT-C Trial: pegylated interferon as maintenance therapy for chronic hepatitis C in previous interferon nonresponders. Control Clin Trials. 2004;25:472–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-DK-9-2325/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 025780-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2323/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2326/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
