The structural biology of Toll-like receptors
- PMID: 21481769
- PMCID: PMC3075535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2011.02.004
The structural biology of Toll-like receptors
Abstract
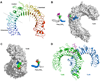
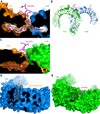
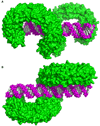
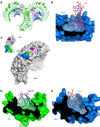
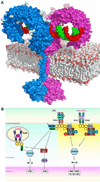
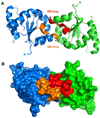
The membrane-bound Toll-like receptors (TLRs) trigger innate immune responses after recognition of a wide variety of pathogen-derived compounds. Despite the wide range of ligands recognized by TLRs, the receptors share a common structural framework in their extracellular, ligand-binding domains. These domains all adopt horseshoe-shaped structures built from leucine-rich repeat motifs. Typically, on ligand binding, two extracellular domains form an "m"-shaped dimer sandwiching the ligand molecule bringing the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains in close proximity and triggering a downstream signaling cascade. Although the ligand-induced dimerization of these receptors has many common features, the nature of the interactions of the TLR extracellular domains with their ligands varies markedly between TLR paralogs.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K. TLR accessory molecules. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008;20:420–425. - PubMed
-
- Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T, Kamano S, Gober HJ, Okamoto K, Nishikawa K, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Aoki K, Ohya K, Imai Y, Morishita Y, Miyazono K, Kato S, Saftig P, Takayanagi H. Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science. 2008;319:624–627. - PubMed
-
- Bell JK, Mullen GE, Leifer CA, Mazzoni A, Davies DR, Segal DM. Leucine-rich repeats and pathogen recognition in Toll-like receptors. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:528–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

