Deletion of p120-catenin results in a tumor microenvironment with inflammation and cancer that establishes it as a tumor suppressor gene
- PMID: 21481789
- PMCID: PMC3077713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.007
Deletion of p120-catenin results in a tumor microenvironment with inflammation and cancer that establishes it as a tumor suppressor gene
Abstract
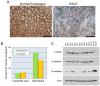
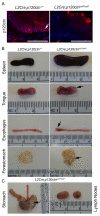
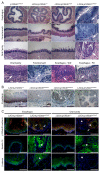
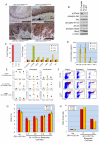
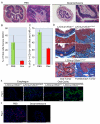
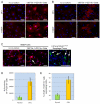
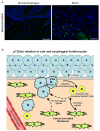
p120-catenin (p120ctn) interacts with E-cadherin, but to our knowledge, no formal proof that p120ctn functions as a bona fide tumor suppressor gene has emerged to date. We report herein that p120ctn loss leads to tumor development in mice. We have generated a conditional knockout model of p120ctn whereby mice develop preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in the oral cavity, esophagus, and squamous forestomach. Tumor-derived cells secrete granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα). The tumors contain significant desmoplasia and immune cell infiltration. Immature myeloid cells comprise a significant percentage of the immune cells present and likely participate in fostering a favorable tumor microenvironment, including the activation of fibroblasts.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
The unholy trinity: inflammation, cytokines, and STAT3 shape the cancer microenvironment.Cancer Cell. 2011 Apr 12;19(4):429-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.03.018. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 21481782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastasiadis PZ, Moon SY, Thoreson MA, Mariner DJ, Crawford HC, Zheng Y, Reynolds AB. Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:637–644. - PubMed
-
- Andl CD, Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Oyama K, Harada H, Chruma K, Herlyn M, Rustgi AK. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1824–1830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- CA111947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA095103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK069984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA115299/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA143056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA143056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055724/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA115299/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA138498/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32-CA1308513/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 50CA95103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA098101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA055724/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA098101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99/R00-CA138498/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA138498/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

