A RasGRP, C. elegans RGEF-1b, couples external stimuli to behavior by activating LET-60 (Ras) in sensory neurons
- PMID: 21482356
- PMCID: PMC3081643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.039
A RasGRP, C. elegans RGEF-1b, couples external stimuli to behavior by activating LET-60 (Ras) in sensory neurons
Abstract
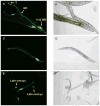
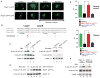
RasGRPs, which load GTP onto Ras and Rap1, are expressed in vertebrate and invertebrate neurons. The functions, regulation, and mechanisms of action of neuronal RasGRPs are unknown. Here, we show how C. elegans RGEF-1b, a prototypical neuronal RasGRP, regulates a critical behavior. Chemotaxis to volatile odorants was disrupted in RGEF-1b-deficient (rgef-1⁻/⁻) animals and wild-type animals expressing dominant-negative RGEF-1b in AWC sensory neurons. AWC-specific expression of RGEF-1b-GFP restored chemotaxis in rgef-1⁻/⁻ mutants. Signals disseminated by RGEF-1b in AWC neurons activated a LET-60 (Ras)-MPK-1 (ERK) signaling cascade. Other RGEF-1b and LET-60 effectors were dispensable for chemotaxis. A bifunctional C1 domain controlled intracellular targeting and catalytic activity of RGEF-1b and was essential for sensory signaling in vivo. Chemotaxis was unaffected when Ca²+-binding EF hands and a conserved phosphorylation site of RGEF-1b were inactivated. Diacylglycerol-activated RGEF-1b links external stimuli (odorants) to behavior (chemotaxis) by activating the LET-60-MPK-1 pathway in specific neurons.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Bargmann CI WormBook, The C. elegans Research Community. Chemosensation in C. elegans. WormBook. 2006 doi: 10.1895/wormbook1.123.1. http://www.wormbook.org. - DOI
-
- Bargmann CI, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;74:515–527. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Horvitz HR. Chemosensory neurons with overlapping functions direct chemotaxis to multiple chemicals in C. elegans. Neuron. 1991;7:729–742. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL, Rehmann H, Wittinghofer A. GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell. 2007;129:865–877. - PubMed
-
- Buday L, Downward J. Many faces of Ras activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1786:178–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

