Major basic protein from eosinophils and myeloperoxidase from neutrophils are required for protective immunity to Strongyloides stercoralis in mice
- PMID: 21482685
- PMCID: PMC3191984
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00931-10
Major basic protein from eosinophils and myeloperoxidase from neutrophils are required for protective immunity to Strongyloides stercoralis in mice
Abstract
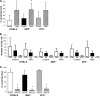
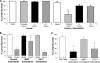
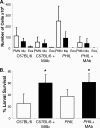
Eosinophils and neutrophils contribute to larval killing during the primary immune response, and neutrophils are effector cells in the secondary response to Strongyloides stercoralis in mice. The objective of this study was to determine the molecular mechanisms used by eosinophils and neutrophils to control infections with S. stercoralis. Using mice deficient in the eosinophil granule products major basic protein (MBP) and eosinophil peroxidase (EPO), it was determined that eosinophils kill the larvae through an MBP-dependent mechanism in the primary immune response if other effector cells are absent. Infecting PHIL mice, which are eosinophil deficient, with S. stercoralis resulted in development of primary and secondary immune responses that were similar to those of wild-type mice, suggesting that eosinophils are not an absolute requirement for larval killing or development of secondary immunity. Treating PHIL mice with a neutrophil-depleting antibody resulted in a significant impairment in larval killing. Naïve and immunized mice with neutrophils deficient in myeloperoxidase (MPO) infected with S. stercoralis had significantly decreased larval killing. It was concluded that there is redundancy in the primary immune response, with eosinophils killing the larvae through an MBP-dependent mechanism and neutrophils killing the worms through an MPO-dependent mechanism. Eosinophils are not required for the development or function of secondary immunity, but MPO from neutrophils is required for protective secondary immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham D., et al. 1995. Strongyloides stercoralis: protective immunity to third-stage larvae in BALB/cByJ mice. Exp. Parasitol. 80:297–307 - PubMed
-
- Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Richardson B. A., Butterworth A. E. 1985. Comparative toxicity of purified human eosinophil granule cationic proteins for schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 34:735–745 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

