Extraneous factors in judicial decisions
- PMID: 21482790
- PMCID: PMC3084045
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018033108
Extraneous factors in judicial decisions
Abstract
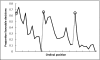
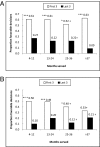
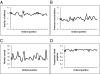
Are judicial rulings based solely on laws and facts? Legal formalism holds that judges apply legal reasons to the facts of a case in a rational, mechanical, and deliberative manner. In contrast, legal realists argue that the rational application of legal reasons does not sufficiently explain the decisions of judges and that psychological, political, and social factors influence judicial rulings. We test the common caricature of realism that justice is "what the judge ate for breakfast" in sequential parole decisions made by experienced judges. We record the judges' two daily food breaks, which result in segmenting the deliberations of the day into three distinct "decision sessions." We find that the percentage of favorable rulings drops gradually from ≈ 65% to nearly zero within each decision session and returns abruptly to ≈ 65% after a break. Our findings suggest that judicial rulings can be swayed by extraneous variables that should have no bearing on legal decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Overlooked factors in the analysis of parole decisions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Oct 18;108(42):E833; author reply E834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110910108. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21987788 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Leiter B. In: The Blackwell Guide to Philosophy of Law and Legal Theory. Edmundson W, Golding M, editors. Oxford: Blackwell; 2005. pp. 50–66.
-
- Neuborne B. Of sausage factories and syllogism machines: Formalism, realism and exclusionary selection techniques. NYU L Rev. 1992;67:419–449.
-
- Holmes OW. The Common Law. Boston: Little, Brown; 1881.
-
- Frank J. Law and the Modern Mind. New York: Brentano's; 1930.
-
- Kozinski A. What I ate for breakfast and other mysteries of judicial decision making. Loyola LA L Rev. 1993;26:993.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

