Meta-analysis indicates that common variants at the DISC1 locus are not associated with schizophrenia
- PMID: 21483435
- PMCID: PMC3359642
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2011.41
Meta-analysis indicates that common variants at the DISC1 locus are not associated with schizophrenia
Abstract
Several polymorphisms in the Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 (DISC1) gene are reported to be associated with schizophrenia. However, to date, there has been little effort to evaluate the evidence for association systematically. We carried out an imputation-driven meta-analysis, the most comprehensive to date, using data collected from 10 candidate gene studies and three genome-wide association studies containing a total of 11 626 cases and 15 237 controls. We tested 1241 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in total, and estimated that our power to detect an effect from a variant with minor allele frequency >5% was 99% for an odds ratio of 1.5 and 51% for an odds ratio of 1.1. We find no evidence that common variants at the DISC1 locus are associated with schizophrenia.
Figures



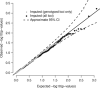

References
-
- Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC. Schizophrenia as a complex trait—evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:1187–1192. - PubMed
-
- Cardno AG, Gottesman II. Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bow-and-arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics. Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs PA, Brunton M, Frackiewicz A, Newton M, Cook PJL, Robson EB. Studies on a family with three cytogenetic markers. Ann Hum Genet. 1970;33:325–336.
-
- St Clair D, Blackwood D, Muir W, Carothers A, Walker M, Spowart G, et al. Association within a family of a balanced autosomal translocation with major mental illness. Lancet. 1990;336:13–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

