XerR, a negative regulator of XccR in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, relieves its repressor function in planta
- PMID: 21483448
- PMCID: PMC3193503
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.64
XerR, a negative regulator of XccR in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, relieves its repressor function in planta
Abstract
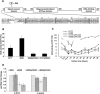
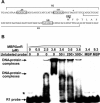
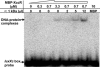
We previously reported that XccR, a LuxR-type regulator of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc), activates the downstream proline iminopeptidase virulence gene (pip) in response to certain host plant factor(s). In this report, we further show that the expression of the xccR gene was repressed in the culture medium by an NtrC-type response regulator, which we named XerR (XccR expression-related, repressor), and that this repression was relieved when the bacteria were grown in planta. Such a regulatory mechanism is reinforced by the observations that XerR directly bound to the xccR promoter in vitro, and that mutations at the phosphorylation-related residues of XerR resulted in the loss of its repressor function. Furthermore, the expression level of xccR increased even in XerR-overexpressing Xcc cells when they were vacuum infiltrated into cabbage plants. We also preliminarily characterized the host factor(s) involved in the above mentioned interactions between Xcc and the host plant, showing that a plant material(s) with molecular weight(s) less than 1 kDa abolished the binding of XerR to the xccR promoter, while the same material enhanced the binding of XccR to the luxXc box in the pip promoter. Taken together, our results implicate XerR in a new layer of the regulatory mechanism controlling the expression of the virulence-related xccR/pip locus and provide clues to the identification of plant signal molecules that interact with XerR and XccR to enhance the virulence of Xcc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytopathogenic bacteria utilize host glucose as a signal to stimulate virulence through LuxR homologues.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Apr;24(4):359-373. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13302. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36762904 Free PMC article.
-
A proline iminopeptidase gene upregulated in planta by a LuxR homologue is essential for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Jul;65(1):121-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05775.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17581124
-
Synergistic activation of the pathogenicity-related proline iminopeptidase gene in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris by HrpX and a LuxR homolog.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Oct;78(19):7069-74. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01726-12. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22865058 Free PMC article.
-
The rsmA-like gene rsmA(Xcc) of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris is involved in the control of various cellular processes, including pathogenesis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008 Apr;21(4):411-23. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-4-0411. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008. PMID: 18321187
-
Flp, a Fis-like protein, contributes to the regulation of type III secretion and virulence processes in the phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris.Mol Plant Pathol. 2019 Aug;20(8):1119-1133. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12818. Epub 2019 May 14. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31090173 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A plant-responsive bacterial-signaling system senses an ethanolamine derivative.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 25;115(39):9785-9790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809611115. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30190434 Free PMC article.
-
Phytopathogenic bacteria utilize host glucose as a signal to stimulate virulence through LuxR homologues.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Apr;24(4):359-373. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13302. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36762904 Free PMC article.
-
Secretome analysis of rice suspension-cultured cells infected by Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryza (Xoo).Proteome Sci. 2016 Feb 2;14:2. doi: 10.1186/s12953-016-0091-z. eCollection 2016. Proteome Sci. 2016. PMID: 26839515 Free PMC article.
-
The inter-kingdom solo OryR regulator of Xanthomonas oryzae is important for motility.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Apr;14(3):211-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00843.x. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23083431 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Screening for Novel Candidate Virulence Related Response Regulator Genes in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 7;9:1789. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01789. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30131784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decho AW, Norman RS, Visscher PT. Quorum sensing in natural environments: emerging views from microbial mats. Trends Microbiol. 2010;18:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Mullard A. Microbiology: Tinker, bacteria, eukaryote, spy. Nature. 2009;459:159–161. - PubMed
-
- Antunes LC, Ferreira RB. Intercellular communication in bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2009;35:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Engebrecht J, Nealson K, Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983;32:773–781. - PubMed
-
- Miller MB, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:165–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

