Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) A Possible Aid for Pain Relief in Developing Countries?
- PMID: 21483510
- PMCID: PMC3066716
- DOI: 10.4176/090119
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) A Possible Aid for Pain Relief in Developing Countries?
Abstract
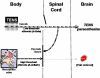
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) refers to the delivery of electrical currents through the skin to activate peripheral nerves. The technique is widely used in developed countries to relieve a wide range of acute and chronic pain conditions, including pain resulting from cancer and its treatment. There are many systematic reviews on TENS although evidence is often inconclusive because of shortcomings in randomised control trials methodology. In this overview the basic science behind TENS will be discussed, the evidence of its effectiveness in specific clinical conditions analysed and a case for its use in pain management in developing countries will be made.
Keywords: Analgesia; Developing countries; Pain; Pain gate theory; Pain management; Pain relief; Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS).
Figures


References
-
- Barlas P., Lundeberg T. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and acupuncture, in Melzack and Wall's Textbook of Pain. In: McMahon S., Koltzenburg M., editors. Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2006. pp. 583–90.
-
- Walsh D. 1st ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1997. TENS.Clinical applications and related theory.
-
- Johnson M. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, in Electrotherapy: Evidence based practice. In: Watson T., editor. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2008. pp. 253–96.
-
- Gildenberg P.L. History of electrical neuromodulation for chronic pain. Pain Med. 2006;7(1):S7–S13.
-
- Melzack R., Wall P. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science. 1965;150:971–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
