Evaluation of renal volume by ultrasonography in patients with essential hypertension in Ile-Ife, south western Nigeria
- PMID: 21483591
- PMCID: PMC3071164
- DOI: 10.3402/ljm.v5i0.4848
Evaluation of renal volume by ultrasonography in patients with essential hypertension in Ile-Ife, south western Nigeria
Abstract
Background and aims: To determine renal volume in adult patients with essential hypertension and correlate it with age, sex, body mass index (BMI), body surface area (BSA) and duration of hypertension.
Patients and methods: A total of 150 patients (75 males, 75 females) with essential hypertension and normal renal status were evaluated sonographically in this prospective study. Fifty healthy individuals (25 males, 25 females) without hypertension were also evaluated as control. Renal volume was then calculated from the kidney's length, width and anterio-posterior diameter using the formula L×W×AP×0.523.
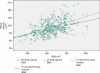
Results: The range of renal volume obtained was 51.65-205.02 cm(3), with a mean of 114.06 ± 29.78 cm(3) for the left kidney and 47.37-177.50 cm(3) with a mean of 106.14 ± 25.42 cm(3) for the right kidney. The mean volumes of the right and left kidneys in males (112.98 ± 25.56 cm(3) and 123.11 ± 32.49 cm(3), respectively), were significantly higher than in females (99.31 ± 23.07 cm(3) and 105.01 ± 23.77 cm(3), respectively). Renal volume correlated significantly with BSA and BMI, but decreased with age. The renal volume showed no correlation with duration of hypertension.
Conclusion: Renal volume is higher in the left than the right kidney in hypertensive patients of both sexes and female hypertensive patients have smaller kidney size compared to males. The study also shows that volume of both kidneys decreases with age and positive correlation between renal volume, BSA and BMI. However, there is no correlation between renal size and duration of hypertension.
Keywords: essential hypertension; renal volume; ultrasonography.
Figures
References
-
- Singh GR, Wendy EH. Kidney volume, blood pressure and albuminuria; findings in an Australia aboriginal community. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:254–9. - PubMed
-
- Akinkugbe OO, editor. Non-communicable diseases in Nigeria; series 1. Nigeria: Federal Ministry of Health and Human Services; 1992. pp. 2–24.
-
- Bakker J, Olree M, Kaatee R, de Lange EE, Moons KG, Beutler JJ, et al. Renal volume measurement; accuracy and repeatability of ultrasound compared with that of MR imaging. Radiology. 1999;211:623–8. - PubMed
-
- White ME, Choyke PL. Duplex sonography of the abdomen. In: Grant EG, White EM, editors. Duplex sonography. New York: Springer; 1988. pp. 129–90.
-
- Pontremoli R, Viazzi F, Martinoli C, Ravera M, Nicolella C, Berruti V, et al. Increased renal resistive index in patients with essential hypertension; a marker of target organ damage. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:360–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources