Label-free high-resolution imaging of prostate glands and cavernous nerves using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy
- PMID: 21483613
- PMCID: PMC3072130
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.2.000915
Label-free high-resolution imaging of prostate glands and cavernous nerves using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy
Abstract
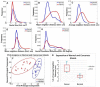
A custom built coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscope was used to image prostatic glands and nerve structures from 17 patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Imaging of glandular and nerve structures showed distinctive cellular features that correlated to histological stains. Segmentation of cell nucleus was performed to establish a cell feature-based model to separate normal glands from cancer glands. In this study, we use a single parameter, average cell neighbor distance based on CARS imaging, to characterize normal and cancerous glandular structures. By combining CARS with our novel classification model, we are able to characterize prostate glandular and nerve structures in a manner that potentially enables real-time, intra-operative assessment of surgical margins and neurovascular bundles. As such, this method could potentially improve outcomes following radical prostatectomy.
Keywords: (170.1610) Clinical applications; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.4580) Optical diagnostics for medicine; (180.4315) Nonlinear microscopy.
Figures






References
-
- W. International Agency for Research on Cancer, “Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide in 2008” (2008), http://globocan.iarc.fr/
-
- Grossfeld G. D., Chang J. J., Broering J. M., Miller D. P., Yu J., Flanders S. C., Henning J. M., Stier D. M., Carroll P. R., “Impact of positive surgical margins on prostate cancer recurrence and the use of secondary cancer treatment: data from the CaPSURE database,” J. Urol. 163(4), 1171–1177, quiz 1295 (2000). 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67716-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
