Role of heparanase on hepatic uptake of intestinal derived lipoprotein and fatty streak formation in mice
- PMID: 21483695
- PMCID: PMC3070732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018370
Role of heparanase on hepatic uptake of intestinal derived lipoprotein and fatty streak formation in mice
Abstract
Background: Heparanase modulates the level of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) which have an important role in multiple cellular processes. Recent studies indicate that HSPGs have an important function in hepatic lipoprotein handling and processes involving removal of lipoprotein particles.
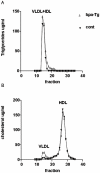
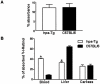
Principal findings: To determine the effects of decreased HSPGs chain length on lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis, transgenic mice over-expressing the human heparanase gene were studied. Hepatic lipid uptake in hpa-Tg mice were evaluated by giving transgenic mice oral fat loads and labeled retinol. Sections of aorta from mice over-expressing heparanase (hpa-Tg) and controls (C57/BL6) fed an atherogenic diet were examined for evidence of atherosclerosis. Heparanase over-expression results in reduced hepatic clearance of postprandial lipoproteins and higher levels of fasting and postprandial serum triglycerides. Heparanase over-expression also induces formation of fatty streaks in the aorta. The mean lesion cross-sectional area in heparanase over-expressing mice was almost 6 times higher when compared to control mice (23,984 µm(2)±5,922 vs. 4,189 µm(2)±1,130, p<0.001).
Conclusions: Over-expression of heparanase demonstrates the importance of HSPGs for the uptake of intestinal derived lipoproteins and its role in the formation of fatty streaks.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

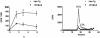

Similar articles
-
Heparanase inhibition attenuates atherosclerosis progression and liver steatosis in E0 mice.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Sep;276:155-162. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.07.026. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 30075439
-
Heparanase is expressed in osteoblastic cells and stimulates bone formation and bone mass.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Jun;207(3):784-92. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20625. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16514606
-
Inflammatory cytokines and fatty acids regulate endothelial cell heparanase expression.Biochemistry. 2004 May 4;43(17):4971-7. doi: 10.1021/bi0356552. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15109255
-
Involvement of heparanase in atherosclerosis and other vessel wall pathologies.Matrix Biol. 2013 Jun 24;32(5):241-51. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23499530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Heparan Sulfate and Heparanase in Amyloid Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1221:631-645. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34521-1_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32274729 Review.
Cited by
-
Heparanase: A Novel Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis.Cells. 2022 Oct 12;11(20):3198. doi: 10.3390/cells11203198. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia alters liver glycosaminoglycans and associated-lipoprotein receptors in rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2017 Nov;73(4):539-550. doi: 10.1007/s13105-017-0583-z. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28762182
-
Heparanase Inhibition Prevents Liver Steatosis in E0 Mice.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 17;11(6):1672. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061672. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35329997 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating intestinal function to reduce atherogenic lipoproteins.Clin Lipidol. 2013 Aug 1;8(4):10.2217/clp.13.40. doi: 10.2217/clp.13.40. Clin Lipidol. 2013. PMID: 24409204 Free PMC article.
-
Blood transcriptomic biomarkers of alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Framingham Heart Study.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Jan 27;32(4):649-658. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac237. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36130209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vlodavsky I, Korner G, Ishai-Michaeli R, Bashkin P, Bar-Shavit R, et al. Extracellular matrix-resident growth factors and enzymes: possible involvement in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990;9:203–226. - PubMed
-
- Williams KJ, Fuki IV. Cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans: dynamic molecules mediating ligand catabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8:253–262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

