Four-year treatment outcomes of adult patients enrolled in Mozambique's rapidly expanding antiretroviral therapy program
- PMID: 21483703
- PMCID: PMC3070740
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018453
Four-year treatment outcomes of adult patients enrolled in Mozambique's rapidly expanding antiretroviral therapy program
Abstract
Background: In Mozambique during 2004-2007 numbers of adult patients (≥15 years old) enrolled on antiretroviral therapy (ART) increased about 16-fold, from <5,000 to 79,500. All ART patients were eligible for co-trimoxazole. ART program outcomes, and determinants of outcomes, have not yet been reported.
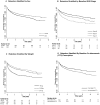
Methodology/principal findings: In a retrospective cohort study, we investigated rates of mortality, attrition (death, loss to follow-up, or treatment cessation), immunologic treatment failure, and regimen-switch, as well as determinants of selected outcomes, among a nationally representative sample of 2,596 adults initiating ART during 2004-2007. At ART initiation, median age of patients was 34 and 62% were female. Malnutrition and advanced disease were common; 18% of patients weighed <45 kilograms, and 15% were WHO stage IV. Median baseline CD4(+) T-cell count was 153/µL and was lower for males than females (139/µL vs. 159/µL, p<0.01). Stavudine, lamivudine, and nevirapine or efavirenz were prescribed to 88% of patients; only 31% were prescribed co-trimoxazole. Mortality and attrition rates were 3.4 deaths and 19.8 attritions per 100 patient-years overall, and 12.9 deaths and 57.2 attritions per 100 patient-years in the first 90 days. Predictors of attrition included male sex [adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) 1.5; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.3-1.8], weight <45 kg (AHR 2.1; 95% CI, 1.6-2.9, reference group >60 kg), WHO stage IV (AHR 1.7; 95% CI, 1.3-2.4, reference group WHO stage I/II), lack of co-trimoxazole prescription (AHR 1.4; 95% CI, 1.0-1.8), and later calendar year of ART initiation (AHR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.8). Rates of immunologic treatment failure and regimen-switch were 14.0 and 0.6 events per 100-patient years, respectively.
Conclusions: ART initiation at earlier disease stages and scale-up of co-trimoxazole among ART patients could improve outcomes. Research to determine reasons for low regimen-switch rates and increasing rates of attrition during program expansion is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Towards universal access: Scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector - Progress report. 2010. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2010. Avaliable: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/2010progressreport/en/. Accessed 29 January 2011.
-
- Bennett S, Boerma JT, Brugha R. Scaling up HIV/AIDS evaluation. Lancet. 2006;367:79–82. - PubMed
-
- Laurent C, Ngom Gueye NF, Ndour CT, Gueye PM, Diouf M, et al. Long-term benefits of highly active antiretroviral therapy in Senegalese HIV-1-infected adults. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;38:14–17. - PubMed
-
- Ferradini L, Jeannin A, Pinoges L, Izopet J, Odhiambo D, et al. Scaling up of highly active antiretroviral therapy in a rural district of Malawi: an effectiveness assessment. Lancet. 2006;367:1335–1342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials