Cancer-associated splicing variant of tumor suppressor AIMP2/p38: pathological implication in tumorigenesis
- PMID: 21483803
- PMCID: PMC3069106
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001351
Cancer-associated splicing variant of tumor suppressor AIMP2/p38: pathological implication in tumorigenesis
Abstract
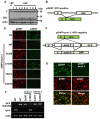
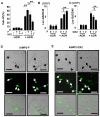
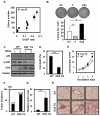
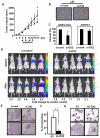
Although ARS-interacting multifunctional protein 2 (AIMP2, also named as MSC p38) was first found as a component for a macromolecular tRNA synthetase complex, it was recently discovered to dissociate from the complex and work as a potent tumor suppressor. Upon DNA damage, AIMP2 promotes apoptosis through the protective interaction with p53. However, it was not demonstrated whether AIMP2 was indeed pathologically linked to human cancer. In this work, we found that a splicing variant of AIMP2 lacking exon 2 (AIMP2-DX2) is highly expressed by alternative splicing in human lung cancer cells and patient's tissues. AIMP2-DX2 compromised pro-apoptotic activity of normal AIMP2 through the competitive binding to p53. The cells with higher level of AIMP2-DX2 showed higher propensity to form anchorage-independent colonies and increased resistance to cell death. Mice constitutively expressing this variant showed increased susceptibility to carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis. The expression ratio of AIMP2-DX2 to normal AIMP2 was increased according to lung cancer stage and showed a positive correlation with the survival of patients. Thus, this work identified an oncogenic splicing variant of a tumor suppressor, AIMP2/p38, and suggests its potential for anti-cancer target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Stetefeld J, Ruegg MA. Structural and functional diversity generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:515–521. - PubMed
-
- Nissim-Rafinia M, Kerem B. The splicing machinery is a genetic modifier of disease severity. Trends Genet. 2005;21:480–483. - PubMed
-
- Schwerk C, Schulze-Osthoff K. Regulation of apoptosis by alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2005;19:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Park SG, Ewalt KL, Kim S. Functional expansion of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and their interacting factors: new perspectives on housekeepers. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:569–574. - PubMed
-
- Lee SW, Cho BH, Park SG, Kim S. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complexes: beyond translation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:3725–3734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

