α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the early postnatal mouse superior cervical ganglion
- PMID: 21485013
- PMCID: PMC3141087
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.20870
α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the early postnatal mouse superior cervical ganglion
Abstract
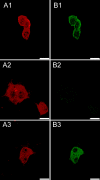
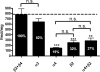
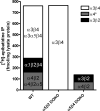
Heteropentameric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) mediate fast synaptic transmission in ganglia of the autonomic nervous system. It is undisputed that α3 and β4 are the predominant subunits in the superior cervical ganglion (SCG); however, reports on the presence of receptors that contain α4 have been controversial. Here, we have searched for the presence of α4-containing nAChRs in the postnatal rat and mouse SCG. We now show by immunoprecipitation combined with radioligand binding that α4-containing receptors constitute about 20% of hetero-oligomeric nAChRs in postnatal Day 3 (P3) mice. However, already by P9, the level of α4 approaches zero. In contrast, the number of α4-containing receptors is close to zero in the rat SCG at all times investigated. Deletion of the β2 subunit by using α5β2-double knockout (KO) mice removes all α4-containing receptors, suggesting that in the postnatal mouse SCG, α4 co-assembles only with β2 but not with β4. α4β2 receptors are, on the other hand, up-regulated in the SCG of P3 α5β4-double KO mice, where they make up about 50% of receptors that bind [(3) H]-epibatidine. Nonetheless, receptors on the surface of SCG neurons from α5β4-double KO mice maintained for one to two days in culture comprise <10% of α4β2 and >90% of α3β2, as determined by patch clamp recordings with α4β2- and α3β2-specific ligands. We propose that in the P3 SCG of wild type mice, α3β4 (±α5) represent about 62% of receptors, whereas 17% are α3β2β4, and 21% are α4β2 (±α5) receptors.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Bansal A, Singer JH, Hwang BJ, Xu W, Beaudet A, Feller MB. Mice lacking specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits exhibit dramatically altered spontaneous activity patterns and reveal a limited role for retinal waves in forming ON and OFF circuits in the inner retina. J Neurosci. 2000;20:7672–7681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cartier GE, Yoshikami D, Gray WR, Luo S, Olivera BM, McIntosh JM. A new α-conotoxin which targets α3β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:7522–7528. - PubMed
-
- Champtiaux N, Changeux J-P. Knockout and knockin mice to investigate the role of nicotinic receptors in the central nervous system. Progr Brain Res. 2004;145:235–251. - PubMed
-
- Champtiaux N, Gotti C, Cordero-Erausquin M, David DJ, Przybylski C, Lena C, Clementi F, Moretti M, Rossi FM, Le Novere N, McIntosh JM, Gardier AM, Changeux J-P. Subunit composition of functional nicotinic receptors in dopaminergic neurons investigated with knock-out mice. J Neurosci. 2003;23:7820–7829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chavez-Noriega LE, Crona JH, Washburn MS, Urrutia A, Elliott KJ, Johnson EC. Pharmacological characterization of recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors hα2β2, hα2β4, hα3β2, hα3β4, hα4β2, hα4β4, and hα7 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;280:346–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

