Peripheral effects of morphine and expression of μ-opioid receptors in the dorsal root ganglia during neuropathic pain: nitric oxide signaling
- PMID: 21486477
- PMCID: PMC3094254
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-25
Peripheral effects of morphine and expression of μ-opioid receptors in the dorsal root ganglia during neuropathic pain: nitric oxide signaling
Abstract
Background: The local administration of μ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonists attenuates neuropathic pain but the precise mechanism implicated in this effect is not completely elucidated. We investigated if nitric oxide synthesized by neuronal (NOS1) or inducible (NOS2) nitric oxide synthases could modulate the local antiallodynic effects of morphine through the peripheral nitric oxide-cGMP-protein kinase G (PKG)-ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channels signaling pathway activation and affect the dorsal root ganglia MOR expression during neuropathic pain.
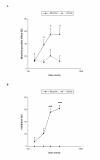
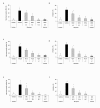
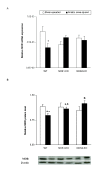
Results: In wild type (WT) mice, the subplantar administration of morphine dose-dependently decreased the mechanical and thermal allodynia induced by the chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve (CCI), which effects were significantly diminished after their co-administration with different subanalgesic doses of a selective NOS1 (N-[(4S)-4-amino-5-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]pentyl]-N'-nitroguanidine tris(trifluoroacetate) salt; NANT), NOS2 (L-N(6)-(1-iminoethyl)-lysine; L-NIL), L-guanylate cyclase (1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one; ODQ), PKG ((Rp)-8-(para-chlorophenylthio)guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate; Rp-8-pCPT-cGMPs) inhibitor or a KATP channel blocker (glibenclamide). The evaluation of the expression of MOR in the dorsal root ganglia from sham-operated and sciatic nerve-injured WT, NOS1 knockout (KO) and NOS2-KO mice at 21 days after surgery demonstrated that, although the basal mRNA and protein levels of MOR were similar between WT and both NOS-KO animals, nerve injury only decreased their expression in WT mice.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the peripheral nitric oxide-cGMP-PKG-KATP signaling pathway activation participates in the local antiallodynic effects of morphine after sciatic nerve injury and that nitric oxide, synthesized by NOS1 and NOS2, is implicated in the dorsal root ganglia down-regulation of MOR during neuropathic pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of nitric oxide in the local antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects and expression of delta-opioid and cannabinoid-2 receptors during neuropathic pain in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Sep 1;334(3):887-96. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.167585. Epub 2010 May 24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20498253
-
The antinociceptive effects of JWH-015 in chronic inflammatory pain are produced by nitric oxide-cGMP-PKG-KATP pathway activation mediated by opioids.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026688. Epub 2011 Oct 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22031841 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibition of the nitric oxide-cGMP-PKG-JNK signaling pathway avoids the development of tolerance to the local antiallodynic effects produced by morphine during neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 15;685(1-3):42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.04.009. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22546233
-
Targeting the nitric oxide/cGMP signaling pathway to treat chronic pain.Neural Regen Res. 2023 May;18(5):996-1003. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.355748. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36254980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and their interactions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jul 6;96(14):7731-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7731. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10393889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antinociceptive modulation by the adhesion GPCR CIRL promotes mechanosensory signal discrimination.Elife. 2020 Sep 30;9:e56738. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56738. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32996461 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of opioid-induced feeding behavior by endogenous nitric oxide in neonatal layer-type chicks.Vet Res Commun. 2015 Jun;39(2):105-13. doi: 10.1007/s11259-015-9631-8. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Vet Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25677536
-
Medial prefrontal cortex nitric oxide modulates neuropathic pain behavior through mu opioid receptors in rats.Korean J Pain. 2022 Oct 1;35(4):413-422. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.4.413. Korean J Pain. 2022. PMID: 36175340 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of Genomic Pathways Based on Differential DNA Methylation Associated With Chronic Postsurgical Pain and Anxiety in Children: A Prospective, Pilot Study.J Pain. 2019 Jul;20(7):771-785. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.12.008. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Pain. 2019. PMID: 30639570 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid 1 and mu-Opioid Receptor Agonists Synergistically Inhibit Abdominal Pain and Lack Side Effects in Mice.J Neurosci. 2022 Aug 17;42(33):6313-6324. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0641-22.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35790401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obara I, Parkitna JR, Korostynski M, Makuch W, Kaminska D, Przewlocka B, Przewlocki R. Local peripheral opioid effects and expression of opioid genes in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia in neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Pain. 2009;141:283–291. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.12.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanabe M, Nagatani Y, Saitoh K, Takasu K, Ono H. Pharmacological assessments of nitric oxide synthase isoforms and downstream diversity of NO signaling in the maintenance of thermal and mechanical hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:702–708. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.12.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

