Vector-mediated release of GABA attenuates pain-related behaviors and reduces Na(V)1.7 in DRG neurons
- PMID: 21486703
- PMCID: PMC3321314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2011.03.007
Vector-mediated release of GABA attenuates pain-related behaviors and reduces Na(V)1.7 in DRG neurons
Abstract
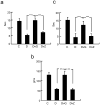
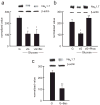
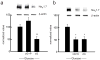
Pain is a common and debilitating accompaniment of neuropathy that occurs as a complication of diabetes. In the current study, we examined the effect of continuous release of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), achieved by gene transfer of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67) to dorsal root ganglia (DRG) in vivo using a non-replicating herpes simplex virus (HSV)-based vector (vG) in a rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN). Subcutaneous inoculation of vG reduced mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia and cold allodynia in rats with PDN. Continuous release of GABA from vector transduced cells in vivo prevented the increase in the voltage-gated sodium channel isoform 1.7 (Na(V)1.7) protein that is characteristic of PDN. In vitro, infection of primary DRG neurons with vG prevented the increase in Na(V)1.7 resulting from exposure to hyperglycemia. The effect of vector-mediated GABA on Na(V)1.7 levels in vitro was blocked by phaclofen but not by bicuculline, a GABA(B) receptor effect that was blocked by pertussis toxin-(PTX) interference with Gα((i/o)) function. Taken in conjunction with our previous observation that continuous activation of delta opioid receptors by vector-mediated release of enkephalin also prevents the increase in Na(V)1.7 in DRG exposed to hyperglycemia in vitro or in vivo, the observations in this report suggest a novel common mechanism through which activation of G protein coupled receptors (GPCR) in DRG neurons regulate the phenotype of the primary afferent.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
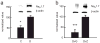
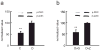
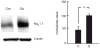
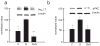
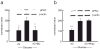
References
-
- Baron R. Peripheral neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to symptoms. Clin J Pain. 2000;16:S12–20. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Liu S, Tanaka M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. Changes in the expression of tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels within dorsal root ganglia neurons in inflammatory pain. Pain. 2004;108:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Castro-Lopes JM, Malcangio M, Pan BH, Bowery NG. Complex changes of GABAA and GABAB receptor binding in the spinal cord dorsal horn following peripheral inflammation or neurectomy. Brain Res. 1995;679:289–297. - PubMed
-
- Castro-Lopes JM, Tavares I, Coimbra A. GABA decreases in the spinal cord dorsal horn after peripheral neurectomy. Brain Res. 1993;620:287–291. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay M, Goss J, Lacomis D, Goins W, Glorioso JC, Mata M, Fink DJ. Protective effect of HSV-mediated gene transfer of nerve growth factor in pyridoxine neuropathy demonstrates functional activity of trkA receptors in large sensory neurons of adult animals. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:732–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

