Changes in muscle sympathetic nerve activity and vascular responses evoked in the spinotrapezius muscle of the rat by systemic hypoxia
- PMID: 21486771
- PMCID: PMC3098710
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201814
Changes in muscle sympathetic nerve activity and vascular responses evoked in the spinotrapezius muscle of the rat by systemic hypoxia
Abstract
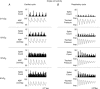
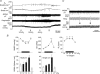
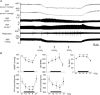
Responses evoked in muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) by systemic hypoxia have received relatively little attention. Moreover, MSNA is generally identified from firing characteristics in fibres supplying whole limbs: their actual destination is not determined. We aimed to address these limitations by using a novel preparation of spinotrapezius muscle in anaesthetised rats. By using focal recording electrodes, multi-unit and discriminated single unit activity were recorded from the surface of arterial vessels.This had cardiac- and respiratory-related activities expected of MSNA, and was increased by baroreceptor unloading, decreased by baroreceptor stimulation and abolished by autonomic ganglion blockade. Progressive, graded hypoxia (breathing sequentially 12, 10, 8% O2 for 2min each) evoked graded increases in MSNA.In single units, mean firing frequency increased from 0.2±0.04 in 21% O2 to 0.62 ± 0.14 Hz in8% O2, while instantaneous frequencies ranged from 0.04–6Hz in 21% O2 to 0.09–20 Hz in 8%O2. Concomitantly, arterial pressure (ABP), fell and heart rate (HR) and respiratory frequency(RF) increased progressively, while spinotrapezius vascular resistance (SVR) decreased (Spinotrapezius blood flow/ABP), indicating muscle vasodilatation. During 8% O2 for 10 min, the falls in ABP and SVR were maintained, but RF, HR and MSNA waned towards baselines from the second to the tenth minute. Thus, we directly show that MSNA increases during systemic hypoxia to an extent that is mainly determined by the increases in peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation and respiratory drive, but its vasoconstrictor effects on muscle vasculature are largely blunted by local dilator influences, despite high instantaneous frequencies in single fibres.
Figures



References
-
- Blumberg H, Janig W, Rieckmann C, Szulczyk P. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes in postganglionic neurones supplying skeletal muscle and hairy skin. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1980;2:223–240. - PubMed
-
- Brock JA, Cunnane TC. Impulse conduction in sympathetic nerve terminals in the guinea-pig vas deferens and the role of the pelvic ganglia. Neuroscience. 1992;47:185–196. - PubMed
-
- Brock JA, Cunnane TC. Neurotransmitter release mechanisms at the sympathetic neuroeffector junction. Exp Physiol. 1993;78:591–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

