High-dose zidovudine plus valganciclovir for Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-associated multicentric Castleman disease: a pilot study of virus-activated cytotoxic therapy
- PMID: 21487108
- PMCID: PMC3143547
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-317610
High-dose zidovudine plus valganciclovir for Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-associated multicentric Castleman disease: a pilot study of virus-activated cytotoxic therapy
Abstract
Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV)-associated multicentric Castleman disease (MCD) is a lymphoproliferative disorder most commonly observed in HIV-infected patients. It is characterized by KSHV-infected plasmablasts that frequently express lytic genes. Patients manifest inflammatory symptoms attributed to overproduction of KSHV viral IL-6, human IL-6, and human IL-6. There is no standard therapy and no established response criteria. We investigated an approach targeting 2 KSHV lytic genes, ORF36 and ORF21, the protein of which, respectively, phosphorylate ganciclovir and zidovudine to toxic moieties. In a pilot study, 14 HIV-infected patients with symptomatic KSHV-MCD received high-dose zidovudine (600 mg orally every 6 hours) and the oral prodrug, valganciclovir (900 mg orally every 12 hours). Responses were evaluated using new response criteria. A total of 86% of patients attained major clinical responses and 50% attained major biochemical responses. Median progression-free survival was 6 months. With 43 months of median follow-up, overall survival was 86% at 12 months and beyond. At the time of best response, the patients showed significant improvements in C-reactive protein, albumin, platelets, human IL-6, IL-10, and KSHV viral load. The most common toxicities were hematologic. These observations provide evidence that therapy designed to target cells with lytic KSHV replication has activity in KSHV-MCD. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00099073.
Figures
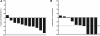

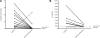
Comment in
-
KSHV: forgotten but not gone.Blood. 2011 Jun 30;117(26):6973-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-350306. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21719604 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oksenhendler E, Duarte M, Soulier J, et al. Multicentric Castleman's disease in HIV infection: a clinical and pathological study of 20 patients. AIDS. 1996;10(1):61–67. - PubMed
-
- Waterston A, Bower M. Fifty years of multicentric Castleman's disease. Acta Oncol. 2004;43(8):698–704. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994;266(5192):1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood. 1995;86(4):1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Teruya-Feldstein J, Zauber P, Setsuda JE, et al. Expression of human herpesvirus-8 oncogene and cytokine homologues in an HIV-seronegative patient with multicentric Castleman's disease and primary effusion lymphoma. Lab Invest. 1998;78(12):1637–1642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

