Single- and cross-commodity discounting among cocaine addicts: the commodity and its temporal location determine discounting rate
- PMID: 21487658
- PMCID: PMC3161151
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2272-x
Single- and cross-commodity discounting among cocaine addicts: the commodity and its temporal location determine discounting rate
Abstract
Rationale: Intertemporal choice has provided important insights into understanding addiction, predicted drug-dependence status, and outcomes of treatment interventions. However, such analyses have largely been based on the choice of a single commodity available either immediately or later (e.g., money now vs. money later). In real life, important choices for those with addiction depend on making decisions across commodities, such as between drug and non-drug reinforcers. To date, no published study has systematically evaluated intertemporal choice using all combinations of a drug and a non-drug commodity.
Objectives: In this study, we examine the interaction between intertemporal choice and commodity type in the decision-making process of cocaine-dependent individuals.
Methods: This study of 47 treatment-seeking cocaine addicts analyzes intertemporal choices of two commodities (equated amounts of cocaine and money), specifically between cocaine now vs. cocaine later (C-C), money now vs. money later (M-M), cocaine now vs. money later (C-M), and money now vs. cocaine later (M-C).
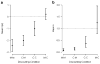
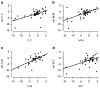
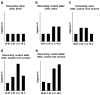
Results: Cocaine addicts discounted significantly more in the C-C condition than in M-M (P = 0.032), consistent with previous reports. Importantly, the two cross-commodity discounting conditions produced different results. Discounting in C-M was intermediate to the C-C and M-M rates, while the greatest degree of discounting occurred in M-C.
Conclusions: These data indicate that the menu of commodities offered alter discounting rates in intertemporal choice and that the greatest rate is obtained when the drug is the later available commodity. Implications for understanding intertemporal choices and addiction are addressed.
Figures
References
-
- Baker F, Johnson MW, Bickel WK. Delay discounting in current and never-before cigarette smokers: similarities and differences across commodity, sign, and magnitude. J Abnorm Psychol. 2003;112:382–392. - PubMed
-
- Bernoulli D. Exposition of a New Theory on the Measurement of Risk. Econometrica. 1954;22:23.
-
- Bickel WK, Marsch LA. Toward a behavioral economic understanding of drug dependence: delay discounting processes. Addiction. 2001;96:73–86. - PubMed
-
- Bickel WK, Amass L, Higgins ST, Badger GJ, Esch RA. Effects of adding behavioral treatment to opioid detoxification with buprenorphine. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1997;65:803–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

