Functional characterization of GNAS mutations found in patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ic defines a new subgroup of pseudohypoparathyroidism affecting selectively Gsα-receptor interaction
- PMID: 21488135
- PMCID: PMC3103608
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.21489
Functional characterization of GNAS mutations found in patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ic defines a new subgroup of pseudohypoparathyroidism affecting selectively Gsα-receptor interaction
Abstract
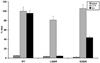
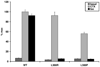
Pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia (PHPIa) is caused by GNAS mutations leading to deficiency of the α-subunit of stimulatory G proteins (Gsα) that mediate signal transduction of G protein-coupled receptors via cAMP. PHP type Ic (PHPIc) and PHPIa share clinical features of Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO); however, in vitro activity of solubilized Gsα protein is normal in PHPIc but reduced in PHPIa. We screened 32 patients classified as PHPIc for GNAS mutations and identified three mutations (p.E392K, p.E392X, p.L388R) in four unrelated families. These and one novel mutation associated with PHPIa (p.L388P) were introduced into a pcDNA3.1(-) expression vector encoding Gsα wild-type and expressed in a Gsα-null cell line (Gnas(E2-/E2-) ). To investigate receptor-mediated cAMP accumulation, we stimulated the endogenous expressed β(2) -adrenergic receptor, or the coexpressed PTH or TSH receptors, and measured the synthesized cAMP by RIA. The results were compared to receptor-independent cholera toxin-induced cAMP accumulation. Each of the mutants associated with PHPIc significantly reduced or completely disrupted receptor-mediated activation, but displayed normal receptor-independent activation. In contrast, PHPIa associated p.L388P disrupted both receptor-mediated activation and receptor-independent activation. We present a new subgroup of PHP that is caused by Gsα deficiency and selectively affects receptor coupling functions of Gsα.
© 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Ahrens W, Hiort O, Staedt P, Kirschner T, Marschke C, Kruse K. Analysis of the GNAS1 gene in Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:4630–4634. - PubMed
-
- Aldred MA. Genetics of pseudohypoparathyroidism types Ia and Ic. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006;19(2):635–640. - PubMed
-
- Bastepe M, Pincus JE, Sugimoto T, Tojo K, Kanatani M, Azuma Y, Kruse K, Rosenbloom AL, Koshiyama H, Jüppner H. Positional dissociation between the genetic mutation responsible for pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ib and the associated methylation defect at exon A/B: evidence for a long-range regulatory element within the imprinted GNAS1 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:1231–1241. - PubMed
-
- Bastepe M, Gunes Y, Perez-Villamil B, Hunzelman J, Weinstein LS, Jüppner H. Receptor-mediated adenylyl cyclase activation through XLalpha(s), the extra-large variant of the stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:1912–1919. - PubMed
-
- Bastepe M, Jüppner H. GNAS locus and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Horm Res. 2005;63:65–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

