Intrinsic and extrinsic control of peripheral T-cell tolerance by costimulatory molecules of the CD28/ B7 family
- PMID: 21488898
- PMCID: PMC3077803
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01011.x
Intrinsic and extrinsic control of peripheral T-cell tolerance by costimulatory molecules of the CD28/ B7 family
Abstract
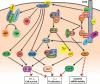
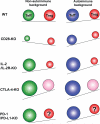
Positive and negative costimulation by members of the CD28 family is critical for the development of productive immune responses against foreign pathogens and their proper termination to prevent inflammation-induced tissue damage. In addition, costimulatory signals are critical for the establishment and maintenance of peripheral tolerance. This paradigm has been established in many animal models and has led to the development of immunotherapies targeting costimulation pathways for the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disease, and allograft rejection. During the last decade, the complexity of the biology of costimulatory pathways has greatly increased due to the realization that costimulation does not affect only effector T cells but also influences regulatory T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Thus, costimulation controls T-cell tolerance through both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. In this review, we discuss the influence of costimulation on intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of peripheral tolerance, with emphasis on members of the CD28 family, CD28, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), and programmed death-1 (PD-1), as well as the downstream cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-2).
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures

References
-
- Mueller DL, Jenkins MK, Schwartz RH. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signaling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. - PubMed
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Salomon B, Bluestone JA. Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225–252. - PubMed
-
- Bluestone JA, St Clair EW, Turka LA. CTLA4Ig: bridging the basic immunology with clinical application. Immunity. 2006;24:233–238. - PubMed
-
- Linsley PS, Nadler SG. The clinical utility of inhibiting CD28-mediated costimulation. Immunol Rev. 2009;229:307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

