Activated IL-23/IL-17 pathway closely correlates with increased Foxp3 expression in livers of chronic hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 21489307
- PMCID: PMC3094328
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-25
Activated IL-23/IL-17 pathway closely correlates with increased Foxp3 expression in livers of chronic hepatitis B patients
Abstract
Background: Foxp3 protein plays a critical role in mediating the inflammatory response and can inhibit the proinflammatory IL-23/IL-17 pathway. However, the molecular interplay of Foxp3 and the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains unclear. To this end, we analyzed the expression patterns of Foxp3- and IL-23/IL-17 pathway-related proinflammatory cytokines in 39 patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure, 71 patients with CHB and 32 healthy controls.
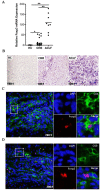
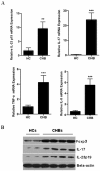
Results: Foxp3 expression was found to be elevated in and mainly expressed by the CD4+ T cell sub-population of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and liver tissues of patients with hepatitis B. The intrahepatic expression of Foxp3 strongly correlated with the copies of HBV DNA and the concentration of surface antigen, HBsAg. IL-23/IL-17 pathway-related proinflammatory cytokines were also found to be significantly increased in patients' liver tissues, as compared to healthy controls. Moreover, Foxp3 expression was strikingly correlated with the production of these cytokines in liver tissues of CHB patients.
Conclusions: The closely-correlated increase of Foxp3 and IL-23/IL-17 pathway activity in HBV-infected livers suggests that the proinflammatory IL-23/IL-17 pathway had not been effectively suppressed by the host immune machinery, such as Treg (Foxp3) cells. Constitutive activation of the IL-23/17 pathway, thus, may support the chronic hepatitis B state.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The balance between intrahepatic IL-17(+) T cells and Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells plays an important role in HBV-related end-stage liver disease.BMC Immunol. 2011 Aug 19;12:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-47. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21851644 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of Treg and Th17 cells balance in the development of acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 May 1;12:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-43. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22548790 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes liver damage via the IL-23/IL-17 axis.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003410. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003410. Epub 2013 Jun 27. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23825942 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating FoxP3+ Regulatory T and Interleukin17-Producing Th17 Cells Actively Influence HBV Clearance in De Novo Hepatitis B Virus Infected Patients after Orthotopic Liver Transplantation.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137881. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2019 Dec 2;14(12):e0226148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226148. PMID: 26367459 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Circulating and liver resident CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 1;177(1):739-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.1.739. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16785573
Cited by
-
Telbivudine treatment corrects HBV-induced epigenetic alterations in liver cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Jan;35(1):53-61. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt317. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24067902 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive diagnostic criteria for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis based on gene expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;54(8):730-741. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01565-x. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30830270
-
Dynamic Changes of Treg and Th17 Cells and Related Cytokines Closely Correlate With the Virological and Biochemical Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Undergoing Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Treatment.Hepat Mon. 2013 Dec 23;13(12):e15332. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.15332. eCollection 2013. Hepat Mon. 2013. PMID: 24403916 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Interleukins in HBV Infection: A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 30;13(12):1675. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121675. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17-A multifaceted cytokine in viral infections.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Dec;236(12):8000-8019. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30471. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34133758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Webster GJ, Reignat S, Brown D, Ogg GS, Jones L, Seneviratne SL, Williams R, Dusheiko G, Bertoletti A. Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: implications for immunotherapy. J Virol. 2004;78:5707–19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.5707-5719.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roncador G, Brown PJ, Maestre L, Hue S, Martinez-Torrecuadrada JL, Ling KL, Pratap S, Toms C, Fox BC, Cerundolo V, Powrie F, Banham AH. Analysis of FOXP3 protein expression in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells at the single-cell level. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:1681–91. doi: 10.1002/eji.200526189. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

