Lipid rafts enriched in monosialylGb5Cer carrying the stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 epitope are involved in development of mouse preimplantation embryos at cleavage stage
- PMID: 21489308
- PMCID: PMC3089780
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-22
Lipid rafts enriched in monosialylGb5Cer carrying the stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 epitope are involved in development of mouse preimplantation embryos at cleavage stage
Abstract
Background: Lipid rafts enriched in glycosphingolipids (GSLs), cholesterol and signaling molecules play an essential role not only for signal transduction started by ligand binding, but for intracellular events such as organization of actin, intracellular traffic and cell polarity, but their functions in cleavage division of preimplantation embryos are not well known.
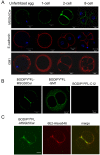
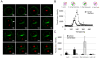
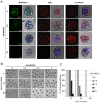
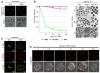
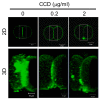
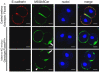
Results: Here we show that monosialylGb5Cer (MSGb5Cer)-enriched raft domains are involved in development during the cleavage stage of mouse preimplantation embryos. MSGb5Cer preferentially localizes at the interfaces between blastomeres in mouse preimplantation embryos. Live-imaging analysis revealed that MSGb5Cer localizes in cleavage furrows during cytokinesis, and that by accumulating at the interfaces, it thickens them. Depletion of cholesterol from the cell membrane with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MbCD) reduced the expression of MSGb5Cer and stopped cleavage. Extensive accumulation of MSGb5Cer at the interfaces by cross-linking with anti-MSGb5Cer Mab (6E2) caused F-actin to aggregate at the interfaces and suppressed the localization of E-cadherin at the interfaces, which resulted in the cessation of cleavage. In addition, suppression of actin polymerization with cytochalasin D (CCD) decreased the accumulation of MSGb5Cer at the interfaces. In E-cadherin-targeted embryos, the MSGb5Cer-enriched raft membrane domains accumulated heterotopically.
Conclusions: These results indicate that MSGb5Cer-enriched raft membrane domains participate in cytokinesis in a close cooperation with the cortical actin network and the distribution of E-cadherin.
© 2011 Sato et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spatio-temporal localization of membrane lipid rafts in mouse oocytes and cleaving preimplantation embryos.Dev Biol. 2007 Mar 15;303(2):727-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.12.009. Epub 2006 Dec 9. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17258703 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lipid rafts in E-cadherin-- and HGF-R/Met--mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells.J Cell Biol. 2004 Aug 30;166(5):743-53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200406078. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15337781 Free PMC article.
-
Fas signaling induces raft coalescence that is blocked by cholesterol depletion in human RPE cells undergoing apoptosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 May;47(5):2172-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1167. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16639029
-
Retrospective analysis: reproducibility of interblastomere differences of mRNA expression in 2-cell stage mouse embryos is remarkably poor due to combinatorial mechanisms of blastomere diversification.Mol Hum Reprod. 2018 Jul 1;24(7):388-400. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gay021. Mol Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29746690
-
[Glycogen metabolism in preimplantation-stage mammalian embryos].Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1982 Aug;83(8):88-95. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1982. PMID: 6816195 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Lipid Signaling During Gamete Maturation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 24;10:814876. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.814876. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36204680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Groups in Infection and Host Susceptibility.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015 Jul;28(3):801-70. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00109-14. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated vesicular trafficking of specific PCDH15 and VLGR1 variants in auditory hair cells.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 3;32(40):13841-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1242-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23035094 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Changes in the Peri-Implantation Period with Mass Spectrometry Imaging: A Systematic Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;13(1):169. doi: 10.3390/life13010169. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-tyrosine kinase signaling in the biological functions associated with sperm.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:181560. doi: 10.1155/2012/181560. Epub 2012 Nov 11. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 23209895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleming TP, Javed Q, Hay M. Epithelial differentiation and intercellular junction formation in the mouse early embryo. Dev Suppl. 1992. pp. 105–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

