Increased expression of transcription factor TFAP2α correlates with chemosensitivity in advanced bladder cancer
- PMID: 21489314
- PMCID: PMC3103475
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-135
Increased expression of transcription factor TFAP2α correlates with chemosensitivity in advanced bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: The standard treatment for patients with advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder is platin based chemotherapy. Only approximately 50% of the patients respond to chemotherapy. Therefore, molecular predictive markers for identification of chemotherapy sensitive subgroups of patients are highly needed. We selected the transcription factor TFAP2α from a previously identified gene expression signature for chemotherapy response.
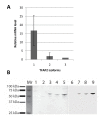
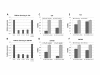
Methods: TFAP2α expression and localization was assessed by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray (TMA) containing 282 bladder cancer tumors from patients with locally advanced (pT2-T4(b) and N(1-3)) or metastatic (M(1)) disease. All patients had received cisplatin containing chemotherapy. Furthermore, QPCR analysis of three TFAP2α isoforms was performed on tumor specimens of advanced muscle invasive bladder cancers (T2-4). Using the bladder cell lines T24 and SW780 the relation of TFAP2α and cisplatin and gemcitabine sensitivity as well as cell proliferation was examined using siRNA directed TFAP2α knockdown.
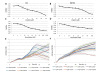
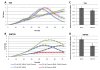
Results: TFAP2α protein expression was analyzed on a TMA with cores from 282 advanced bladder cancer tumors from patients treated with cisplatin based combinational chemotherapy. TFAP2α was identified as a strong independent predictive marker for a good response and survival after cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Strong TFAP2α nuclear and cytoplasmic staining predicted good response to chemotherapy in patients with lymph node metastasis, whereas weak TFAP2α nuclear staining predicted good response in patients without lymph node metastasis. In vitro studies showed that siRNA mediated knockdown of TFAP2α increased the proliferation of SW780 cells and rendered the cells less sensitive to cisplatin and gemcitabine. In contrast to that T24 bladder cells with mutated p53 showed to be more drug sensitive upon TFAP2α depletion.
Conclusions: High levels of nuclear and cytoplasmic TFAP2α protein were a predictor of increased overall survival and progression free survival in patients with advanced bladder cancer treated with cisplatin based chemotherapy. TFAP2α knockdown increased the proliferation of the SW780 bladder cells and reduced cisplatin and gemcitabine induced cell death. The inverse effect was observed in the TP53 mutated T24 cell line where TFAP2α silencing augmented cisplatin and gemcitabine sensitivity and did not stimulate proliferation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pre-clinical and clinical studies on the role of RBM3 in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: longitudinal expression, transcriptome-level effects and modulation of chemosensitivity.BMC Cancer. 2022 Feb 2;22(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09168-7. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35109796 Free PMC article.
-
Biased Expression of the FOXP3Δ3 Isoform in Aggressive Bladder Cancer Mediates Differentiation and Cisplatin Chemotherapy Resistance.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;22(21):5349-5361. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2581. Epub 2016 May 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27189164
-
Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in TP53 subtypes of bladder carcinoma cell lines treated with cisplatin and gemcitabine.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010 Jul;235(7):814-24. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2010.009322. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010. PMID: 20558835
-
Current and future perspectives in advanced bladder cancer: is there a new standard?Semin Oncol. 2002 Feb;29(1 Suppl 3):3-14. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2002.30750. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11894002 Review.
-
Gemcitabine in the treatment of bladder cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):547-53. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.547. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000. PMID: 11249537 Review.
Cited by
-
[Therapy selection in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Is molecular biology helpful?].Urologe A. 2012 Jun;51(6):805-12. doi: 10.1007/s00120-012-2898-2. Urologe A. 2012. PMID: 22576102 German.
-
MiR-193a-5p Targets the Coding Region of AP-2α mRNA and Induces Cisplatin Resistance in Bladder Cancers.J Cancer. 2016 Aug 7;7(12):1740-1746. doi: 10.7150/jca.15620. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27698912 Free PMC article.
-
WWOX Loses the Ability to Regulate Oncogenic AP-2γ and Synergizes with Tumor Suppressor AP-2α in High-Grade Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 12;13(12):2957. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122957. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204827 Free PMC article.
-
Maspin enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity in bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells and correlates with prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients receiving cisplatin based neoadjuvant chemotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 6;35:2. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0282-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26733306 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 15;12(4):684-97. doi: 10.4161/cc.23598. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23343772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Von Der MH, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T. et al.Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4602–4608. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.757. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Von Der MH, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ. et al.Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3068–3077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

