Cancer theranostics: the rise of targeted magnetic nanoparticles
- PMID: 21489647
- PMCID: PMC3210200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.03.001
Cancer theranostics: the rise of targeted magnetic nanoparticles
Abstract
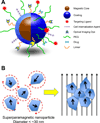
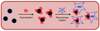
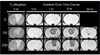
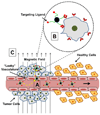
Interest in utilizing magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) for biomedical applications has increased considerably over the past two decades. This excitement has been driven in large part by the success of MNPs as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging. The recent investigative trend with respect to cancer has continued down a diagnostic path, but has also turned toward concurrent therapy, giving rise to the distinction of MNPs as potential "theranostics". Here we review both the key technical principles of MNPs and ongoing advancement toward a cancer theranostic MNP. Recent progress in diagnostics, hyperthermia treatments, and drug delivery are all considered. We conclude by identifying current barriers to clinical translation of MNPs and offer considerations for their future development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors each declare no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Walter P, et al. Early Use of PbS Nanotechnology for an Ancient Hair Dyeing Formula. Nano Letters. 2006;6:2215–2219. - PubMed
-
- Reibold M, et al. Materials: Carbon nanotubes in an ancient Damascus sabre. Nature. 2006;444:286–286. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AK, Gupta M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3995–4021. - PubMed
-
- Schmid Gn, Wiley I. Nanoparticles: from theory to application. Wiley-VCH ; John Wiley; 2004.
-
- Roca AG, et al. Progress in the preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 2009;42:224002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

