Early growth response 1 (Egr-1) regulates phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau in mammalian brain
- PMID: 21489990
- PMCID: PMC3121503
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.220962
Early growth response 1 (Egr-1) regulates phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau in mammalian brain
Abstract
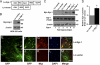
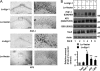
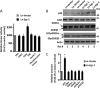
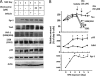
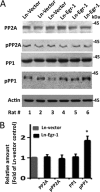
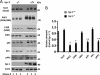
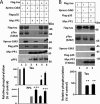
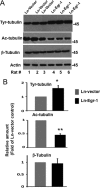
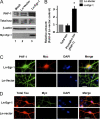
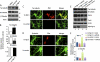
In the normal brain, tau protein is phosphorylated at a number of proline- and non-proline directed sites, which reduce tau microtubule binding and thus regulate microtubule dynamics. In Alzheimer disease (AD), tau is abnormally hyperphosphorylated, leading to neurofibrillary tangle formation and microtubule disruption, suggesting a loss of regulatory mechanisms controlling tau phosphorylation. Early growth response 1 (Egr-1) is a transcription factor that is significantly up-regulated in AD brain. The pathological significance of this up-regulation is not known. In this study, we found that lentivirus-mediated overexpression of Egr-1 in rat brain hippocampus and primary neurons in culture activates proline-directed kinase Cdk5, inactivates PP1, promotes tau phosphorylation at both proline-directed Ser(396/404) and non-proline-directed Ser(262) sites, and destabilizes microtubules. Furthermore, in Egr-1(-/-) mouse brain, Cdk5 activity was decreased, PP1 activity was increased, and tau phosphorylation was reduced at both proline-directed and non-proline-directed sites. By using nerve growth factor-exposed PC12 cells, we determined that Egr-1 activates Cdk5 to promote phosphorylation of tau and inactivates PP1 via phosphorylation. When Cdk5 was inhibited, tau phosphorylation at both proline- and non-proline directed sites and PP1 phosphorylation were blocked, indicating that Egr-1 acts through Cdk5. By using an in vitro kinase assay and HEK-293 cells transfected with tau, PP1, and Cdk5, we found that Cdk5 phosphorylates Ser(396/404) directly. In addition, by phosphorylating and inactivating PP1, Cdk5 promotes tau phosphorylation at Ser(262) indirectly. Our results indicate that Egr-1 is an in vivo regulator of tau phosphorylation and suggest that in AD brain increased levels of Egr-1 aberrantly activate an Egr-1/Cdk5/PP1 pathway, leading to accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau, thus destabilizing the microtubule cytoskeleton.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

