Met receptors induce Sam68-dependent cell migration by activation of alternate extracellular signal-regulated kinase family members
- PMID: 21489997
- PMCID: PMC3122167
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.211409
Met receptors induce Sam68-dependent cell migration by activation of alternate extracellular signal-regulated kinase family members
Abstract
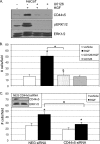
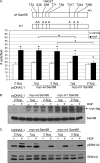
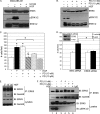
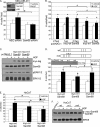
The hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/Met receptor signaling pathway is deregulated in diverse human malignancies and plays a central role in oncogenesis, tumor progression, and invasive cancer growth. Similarly, altered expression and splicing (i.e. inclusion of variant exon 5, "v5") of the cell adhesion marker, CD44, is associated with advanced cancer phenotypes. We sought to further understand how HGF regulates CD44v5 expression. Immortalized nontumorigenic keratinocyte (HaCaT) cells abundantly express both Met receptors and CD44v5 transmembrane glycoproteins. HGF stimulated CD44v5 protein expression and HaCaT cell migration; these events required activation of the ERK1/2 MAPK module and Sam68, a protein involved in RNA processing, splicing, and v5 inclusion. Similar to HaCaT cells, highly migratory MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells also required Sam68 expression for HGF-induced migration. However, MDA-MB-231 cell migration occurred independently of ERK1/2 and CD44v5 expression and instead required ERK5 signaling to Sam68. Phospho-mutant, but not WT-Sam68, blocked HGF-induced cell migration in both cell types; MDA-MB-435 cells behaved similarly. These results suggest that Sam68 acts as a convergence point for ERK signaling to cell migration; blockade of phospho-Sam68 may provide a new avenue for therapeutic inhibition of metastatic cancers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of HGF/Met signaling to Brk and Sam68 in breast cancer progression.Horm Cancer. 2012 Apr;3(1-2):14-25. doi: 10.1007/s12672-011-0097-z. Horm Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22124844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast tumor kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 mediate Met receptor signaling to cell migration in breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(4):R60. doi: 10.1186/bcr2622. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20687930 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxin III suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells.Cell Biochem Funct. 2014 Aug;32(6):485-95. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3041. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014. PMID: 24964901
-
The transcriptional co-activator SND1 is a novel regulator of alternative splicing in prostate cancer cells.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 17;33(29):3794-802. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.360. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23995791
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/MET in cancer progression and biomarker discovery.Cancer Sci. 2017 Mar;108(3):296-307. doi: 10.1111/cas.13156. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28064454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Live-Cell Screen for Altered Erk Dynamics Reveals Principles of Proliferative Control.Cell Syst. 2020 Mar 25;10(3):240-253.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Cell Syst. 2020. PMID: 32191874 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of HGF/Met signaling to Brk and Sam68 in breast cancer progression.Horm Cancer. 2012 Apr;3(1-2):14-25. doi: 10.1007/s12672-011-0097-z. Horm Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22124844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Interaction Between the Oncogenic Kinase NEK2 and Sam68 Promotes a Splicing Program Involved in Migration and Invasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 21;12:880654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.880654. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35530315 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance and Regulation of ERK5 Expression and Function in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;14(2):348. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020348. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Signaling Profiling in a Human Model of Tumorigenic Progression Indicates a Role for Alternative RNA Splicing in Cellular Reprogramming.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 20;19(10):2847. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102847. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30241319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura T., Nawa K., Ichihara A. (1984) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 122, 1450–1459 - PubMed
-
- Russell W. E., McGowan J. A., Bucher N. L. (1984) J. Cell. Physiol. 119, 183–192 - PubMed
-
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. (1987) Nature 327, 239–242 - PubMed
-
- Jiang W., Hiscox S., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. (1999) Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 29, 209–248 - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C., Birchmeier W., Gherardi E., Vande Woude G. F. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 915–925 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

