Significant protection against high-dose simian immunodeficiency virus challenge conferred by a new prime-boost vaccine regimen
- PMID: 21490100
- PMCID: PMC3126289
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00342-11
Significant protection against high-dose simian immunodeficiency virus challenge conferred by a new prime-boost vaccine regimen
Abstract
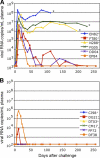
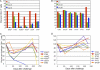
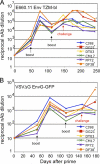
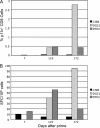
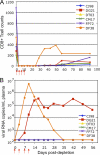
We constructed vaccine vectors based on live recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and a Semliki Forest virus (SFV) replicon (SFVG) that propagates through expression of the VSV glycoprotein (G). These vectors expressing simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) Gag and Env proteins were used to vaccinate rhesus macaques with a new heterologous prime-boost regimen designed to optimize induction of antibody. Six vaccinated animals and six controls were then given a high-dose mucosal challenge with the diverse SIVsmE660 quasispecies. All control animals became infected and had peak viral RNA loads of 10(6) to 10(8) copies/ml. In contrast, four of the vaccinees showed significant (P = 0.03) apparent sterilizing immunity and no detectable viral loads. Subsequent CD8(+) T cell depletion confirmed the absence of SIV infection in these animals. The two other vaccinees had peak viral loads of 7 × 10(5) and 8 × 10(3) copies/ml, levels below those of all of the controls, and showed undetectable virus loads by day 42 postchallenge. The vaccine regimen induced high-titer prechallenge serum neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) to some cloned SIVsmE660 Env proteins, but antibodies able to neutralize the challenge virus swarm were not detected. The cellular immune responses induced by the vaccine were generally weak and did not correlate with protection. Although the immune correlates of protection are not yet clear, the heterologous VSV/SFVG prime-boost is clearly a potent vaccine regimen for inducing virus nAbs and protection against a heterogeneous viral swarm.
Figures
References
-
- Barouch D. H., et al. 2002. Eventual AIDS vaccine failure in a rhesus monkey by viral escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 415:335–339 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

