Reconsolidation or extinction: transcription factor switch in the determination of memory course after retrieval
- PMID: 21490196
- PMCID: PMC6622842
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6066-10.2011
Reconsolidation or extinction: transcription factor switch in the determination of memory course after retrieval
Abstract
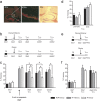
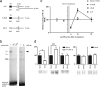
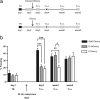
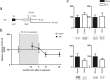
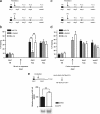
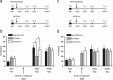
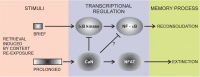
In fear conditioning, aversive stimuli are readily associated with contextual features. A brief reexposure to the training context causes fear memory reconsolidation, whereas a prolonged reexposure induces memory extinction. The regulation of hippocampal gene expression plays a key role in contextual memory consolidation and reconsolidation. However, the mechanisms that determine whether memory will reconsolidate or extinguish are not known. Here, we demonstrate opposing roles for two evolutionarily related transcription factors in the mouse hippocampus. We found that nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is required for fear memory reconsolidation. Conversely, calcineurin phosphatase inhibited NF-κB and induced nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) nuclear translocation in the transition between reconsolidation and extinction. Accordingly, the hippocampal inhibition of both calcineurin and NFAT independently impaired memory extinction, whereas inhibition of NF-κB enhanced memory extinction. These findings represent the first insight into the molecular mechanisms that determine memory reprocessing after retrieval, supporting a transcriptional switch that directs memory toward reconsolidation or extinction. The precise molecular characterization of postretrieval processes has potential importance to the development of therapeutic strategies for fear memory disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcineurin phosphatase as a negative regulator of fear memory in hippocampus: control on nuclear factor-κB signaling in consolidation and reconsolidation.Hippocampus. 2014 Dec;24(12):1549-61. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22334. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 25043904
-
Brain region-specific gene expression activation required for reconsolidation and extinction of contextual fear memory.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 14;29(2):402-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4639-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19144840 Free PMC article.
-
Memory extinction entails the inhibition of the transcription factor NF-kappaB.PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003687. Epub 2008 Nov 10. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18997870 Free PMC article.
-
Brain sites involved in fear memory reconsolidation and extinction of rodents.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Jun;53:160-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25887284 Review.
-
Modulating reconsolidation and extinction to regulate drug reward memory.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Aug;50(3):2503-2512. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14072. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30113098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intra-CA1 administration of FK-506 (tacrolimus) in rat impairs learning and memory in an inhibitory avoidance paradigm.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Feb;18(2):130-7. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25810886 Free PMC article.
-
Can RNA Affect Memory Modulation? Implications for PTSD Understanding and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 17;24(16):12908. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612908. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of transcription in memory consolidation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Dec 4;7(1):a021741. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021741. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25475090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory Reconsolidation Updating in Substance Addiction: Applications, Mechanisms, and Future Prospects for Clinical Therapeutics.Neurosci Bull. 2025 Feb;41(2):289-304. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01294-z. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 39264570 Review.
-
Divergent cellular pathways of hippocampal memory consolidation and reconsolidation.Hippocampus. 2013 Mar;23(3):233-44. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22083. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23197404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albensi BC, Mattson MP. Evidence for the involvement of TNF and NF-kappaB in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Synapse. 2000;35:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Baumgärtel K, Genoux D, Welzl H, Tweedie-Cullen RY, Koshibu K, Livingstone-Zatchej M, Mamie C, Mansuy IM. Control of the establishment of aversive memory by calcineurin and Zif268. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:572–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
