Neuregulin-1 signals from the periphery regulate AMPA receptor sensitivity and expression in GABAergic interneurons in developing neocortex
- PMID: 21490211
- PMCID: PMC6622838
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3477-10.2011
Neuregulin-1 signals from the periphery regulate AMPA receptor sensitivity and expression in GABAergic interneurons in developing neocortex
Abstract
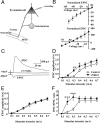
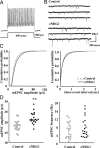
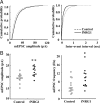
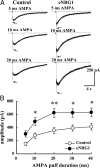
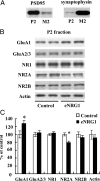
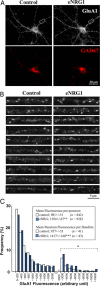
Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) signaling is thought to contribute to both neuronal development and schizophrenia neuropathology. Here, we describe the developmental effects of excessive peripheral NRG1 signals on synaptic activity and AMPA receptor expression of GABAergic interneurons in postnatal rodent neocortex. A core peptide common to all NRG1 variants (eNRG1) was subcutaneously administered to mouse pups. Injected eNRG1 penetrated the blood-brain barrier and activated ErbB4 NRG1 receptors in the neocortex, in which ErbB4 mRNA is predominantly expressed by parvalbumin-positive GABAergic interneurons. We prepared neocortical slices from juvenile mice that were receiving eNRG1 subchronically and recorded inhibitory synaptic activity from layer V pyramidal neurons. Postnatal eNRG1 treatment significantly enhanced polysynaptic IPSCs, although monosynaptic IPSCs were not affected. Examination of excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-containing GABAergic interneurons revealed that eNRG1 treatment significantly increased AMPA-triggered inward currents and the amplitudes and frequencies of miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs). Similar effects on mEPSCs were observed in mice treated with a soluble, full-length form of NRG1 type I. Consistent with the electrophysiologic data, expression of the AMPA receptor GluA1 (i.e., GluR1, GluRA) was upregulated in the postsynaptic density/cytoskeletal fraction prepared from eNRG1-treated mouse neocortices. Cortical GABAergic neurons cultured with eNRG1 exhibited a significant increase in surface GluA1 immunoreactivity at putative synaptic sites on their dendrites. These results indicate that NRG1 circulating in the periphery influences postnatal development of synaptic AMPA receptor expression in cortical GABAergic interneurons and may play a role in conditions characterized by GABA-associated neuropathologic processes.
Figures



References
-
- Abe Y, Namba H, Zheng Y, Nawa H. In situ hybridization reveals developmental regulation of ErbB1–4 mRNA expression in mouse midbrain: implication of ErbB receptors for dopaminergic neurons. Neuroscience. 2009;161:95–110. - PubMed
-
- Barros CS, Calabrese B, Chamero P, Roberts AJ, Korzus E, Lloyd K, Stowers L, Mayford M, Halpain S, Müller U. Impaired maturation of dendritic spines without disorganization of cortical cell layers in mice lacking NRG1/ErbB signaling in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:4507–4512. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buonanno A, Fischbach GD. Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:287–296. - PubMed
-
- Burden S, Yarden Y. Neuregulins and their receptors: a versatile signaling module in organogenesis and oncogenesis. Neuron. 1997;18:847–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
