GABA, its receptors, and GABAergic inhibition in mouse taste buds
- PMID: 21490220
- PMCID: PMC3320853
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5559-10.2011
GABA, its receptors, and GABAergic inhibition in mouse taste buds
Abstract
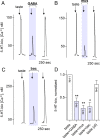
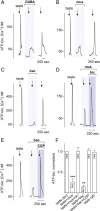
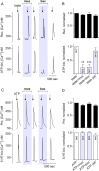
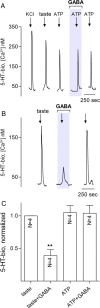
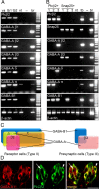
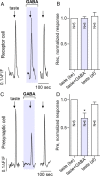
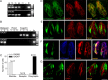
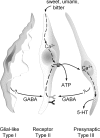
Taste buds consist of at least three principal cell types that have different functions in processing gustatory signals: glial-like (type I) cells, receptor (type II) cells, and presynaptic (type III) cells. Using a combination of Ca2+ imaging, single-cell reverse transcriptase-PCR and immunostaining, we show that GABA is an inhibitory transmitter in mouse taste buds, acting on GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptors to suppress transmitter (ATP) secretion from receptor cells during taste stimulation. Specifically, receptor cells express GABA(A) receptor subunits β2, δ, and π, as well as GABA(B) receptors. In contrast, presynaptic cells express the GABA(A) β3 subunit and only occasionally GABA(B) receptors. In keeping with the distinct expression pattern of GABA receptors in presynaptic cells, we detected no GABAergic suppression of transmitter release from presynaptic cells. We suggest that GABA may serve function(s) in taste buds in addition to synaptic inhibition. Finally, we also defined the source of GABA in taste buds: GABA is synthesized by GAD65 in type I taste cells as well as by GAD67 in presynaptic (type III) taste cells and is stored in both those two cell types. We conclude that GABA is an inhibitory transmitter released during taste stimulation and possibly also during growth and differentiation of taste buds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acid stimulation (sour taste) elicits GABA and serotonin release from mouse taste cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025471. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22028776 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Reduces Taste-Evoked ATP Secretion from Mouse Taste Buds.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12714-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0100-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377461 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate may be an efferent transmitter that elicits inhibition in mouse taste buds.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030662. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22292013 Free PMC article.
-
Taste buds as peripheral chemosensory processors.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Jan;24(1):71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23261954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The molecular aspects of the functional heterogeneity of the GABA receptors].Usp Fiziol Nauk. 1999 Jan-Mar;30(1):29-38. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 1999. PMID: 10205817 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Multiple processes underlie benzodiazepine-mediated increases in the consumption of accepted and avoided stimuli.Chem Senses. 2012 Jun;37(5):431-44. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjr125. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Chem Senses. 2012. PMID: 22248457 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and effects of pulsatile GABA secretion from cytosolic pools in the human beta cell.Nat Metab. 2019 Nov;1(11):1110-1126. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0135-7. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Nat Metab. 2019. PMID: 32432213 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid derivatives as bitter taste receptor (T2R) blockers.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 5;289(36):25054-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.576975. Epub 2014 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25059668 Free PMC article.
-
L-Amino Acids Elicit Diverse Response Patterns in Taste Sensory Cells: A Role for Multiple Receptors.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0130088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130088. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26110622 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic P2X3-containing receptors in gustatory nerve fibres mediate responses to all taste qualities in mice.J Physiol. 2015 Mar 1;593(5):1113-25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.281014. Epub 2015 Jan 20. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25524179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angulo MC, Le Meur K, Kozlov AS, Charpak S, Audinat E. GABA, a forgotten gliotransmitter. Prog Neurobiol. 2008;86:297–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
