Trafficking-deficient hERG K⁺ channels linked to long QT syndrome are regulated by a microtubule-dependent quality control compartment in the ER
- PMID: 21490315
- PMCID: PMC3129823
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00494.2010
Trafficking-deficient hERG K⁺ channels linked to long QT syndrome are regulated by a microtubule-dependent quality control compartment in the ER
Abstract
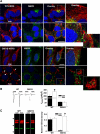
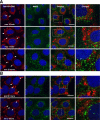
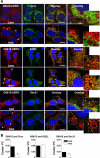
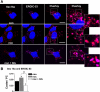
The human ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG) encodes the voltage-gated K(+) channel that underlies the rapidly activating delayed-rectifier current in cardiac myocytes. hERG is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) as an "immature" N-linked glycoprotein and is terminally glycosylated in the Golgi apparatus. Most hERG missense mutations linked to long QT syndrome type 2 (LQT2) reduce the terminal glycosylation and functional expression. We tested the hypothesis that a distinct pre-Golgi compartment negatively regulates the trafficking of some LQT2 mutations to the Golgi apparatus. We found that treating cells in nocodazole, a microtubule depolymerizing agent, altered the subcellular localization, functional expression, and glycosylation of the LQT2 mutation G601S-hERG differently from wild-type hERG (WT-hERG). G601S-hERG quickly redistributed to peripheral compartments that partially colocalized with KDEL (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) chaperones but not calnexin, Sec31, or the ER golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). Treating cells in E-4031, a drug that increases the functional expression of G601S-hERG, prevented the accumulation of G601S-hERG to the peripheral compartments and increased G601S-hERG colocalization with the ERGIC. Coexpressing the temperature-sensitive mutant G protein from vesicular stomatitis virus, a mutant N-linked glycoprotein that is retained in the ER, showed it was not restricted to the same peripheral compartments as G601S-hERG at nonpermissive temperatures. We conclude that the trafficking of G601S-hERG is negatively regulated by a microtubule-dependent compartment within the ER. Identifying mechanisms that prevent the sorting or promote the release of LQT2 channels from this compartment may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for LQT2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacological correction of long QT-linked mutations in KCNH2 (hERG) increases the trafficking of Kv11.1 channels stored in the transitional endoplasmic reticulum.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Nov 1;305(9):C919-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00406.2012. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23864605 Free PMC article.
-
The binding site for channel blockers that rescue misprocessed human long QT syndrome type 2 ether-a-gogo-related gene (HERG) mutations.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4989-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107345200. Epub 2001 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11741928
-
Properties of WT and mutant hERG K(+) channels expressed in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):H1842-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01236.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20363883 Free PMC article.
-
hERG quality control and the long QT syndrome.J Physiol. 2016 May 1;594(9):2469-81. doi: 10.1113/JP270531. Epub 2016 Feb 9. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26718903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress in research on defective protein trafficking and functional restoration in HERG-associated long QT syndrome].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;33(1):101-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2016.01.024. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26829745 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A rare schizophrenia risk variant of CACNA1I disrupts CaV3.3 channel activity.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 19;6:34233. doi: 10.1038/srep34233. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27756899 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a High-Throughput Flow Cytometry Assay to Monitor Defective Trafficking and Rescue of Long QT2 Mutant hERG Channels.Front Physiol. 2018 Apr 19;9:397. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00397. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29725305 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the protein-kinase mediated regulation of the HERG potassium channel synthesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1823(8):1273-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 May 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22613764 Free PMC article.
-
Isogenic human pluripotent stem cell pairs reveal the role of a KCNH2 mutation in long-QT syndrome.EMBO J. 2013 Dec 11;32(24):3161-75. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.240. Epub 2013 Nov 8. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 24213244 Free PMC article.
-
Potassium channels in the heart: structure, function and regulation.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;595(7):2209-2228. doi: 10.1113/JP272864. Epub 2016 Nov 13. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27861921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson CL, Delisle BP, Anson BD, Kilby JA, Will ML, Tester DJ, Gong Q, Zhou Z, Ackerman MJ, January CT. Most LQT2 mutations reduce Kv11.1 (hERG) current by a class 2 (trafficking-deficient) mechanism. Circulation 113: 365–373, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hauri HP. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J Cell Sci 1: 2173–2183, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bolte S, Cordelieres FP. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J Microsc 224: 213–232, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

