Leaky sodium channels from voltage sensor mutations in periodic paralysis, but not paramyotonia
- PMID: 21490317
- PMCID: PMC3100087
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318219fb57
Leaky sodium channels from voltage sensor mutations in periodic paralysis, but not paramyotonia
Abstract
Background: Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (HypoPP) is associated with mutations in either the Ca(V)1.1 calcium channel or the Na(V)1.4 sodium channel. Some Na(V)1.4 HypoPP mutations have been shown to cause an anomalous inward current that may contribute to the attacks of paralysis. Herein, we test whether disease-associated Na(V)1.4 mutations in previously untested homologous regions of the channel also give rise to the anomalous current.
Methods: The functional properties of mutant Na(V)1.4 channels were studied with voltage-clamp techniques in an oocyte expression system.
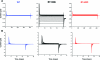
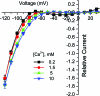
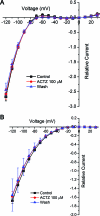
Results: The HypoPP mutation Na(V)1.4-R1132Q conducts an anomalous gating pore current, but the homologous R1448C mutation in paramyotonia congenita does not.
Conclusions: Gating pore currents arising from missense mutations at arginine residues in the voltage sensor domains of Na(V)1.4 are a common feature of HypoPP mutant channels and contribute to the attacks of paralysis.
Figures


Comment on
-
An important piece has been placed in the puzzle of hypokalemic periodic paralysis.Neurology. 2011 May 10;76(19):1614-5. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318219fba9. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21490318 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ptacek LJ, Tawil R, Griggs RC, et al. Dihydropyridine receptor mutations cause hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 1994; 77:863–868 - PubMed
-
- Jurkat-Rott K, Lehmann-Horn F, Albaz A, et al. A calcium channel mutation causing hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3:1415–1419 - PubMed
-
- Sternberg D, Maisonobe T, Jurkat-Rott K, et al. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis type 2 caused by mutations at codon 672 in the muscle sodium channel gene SCN4A. Brain 2001; 124:1091–1099 - PubMed
-
- Bulman DE, Scoggan KA, van Oene MD, et al. A novel sodium channel mutation in a family with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Neurology 1999; 53:1932–1936 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
